In modern diagnostic imaging, understanding what a computed tomography scan is helps us make informed decisions about our health, especially when we are advised to undergo a CT scan in Bangalore at a trusted diagnostic centre.
Many of us feel anxious when a doctor recommends a CT scan, mainly because we are unsure about the procedure, safety, or results. A computed tomography scan is actually one of the most advanced and widely used imaging techniques in modern medicine.
At Koshikaa, knowing what happens before, during, and after the scan can remove fear and replace it with clarity. By the end of this blog, you will clearly understand how a CT scan works and why it plays such a crucial role in accurate diagnosis.
Medical Disclaimer
The information provided in this blog is for general educational and informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. While we aim to share accurate and up-to-date content, it is not a substitute for professional medical consultation, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider or physician regarding any medical condition, symptoms, or health concerns before undergoing a CT scan or any diagnostic procedure.
Key Points at a Glance
- Understand clearly what is a computed tomography scan
- Learn the purpose of computed tomography in medical diagnosis
- Explore the common uses of computed tomography
- Know about the types of computed tomography scans
- Understand computed tomography with contrast
- Get clarity on computed tomography cost and reports
- See how Koshikaa supports safe and accurate CT scanning
What is a Computed Tomography Scan?
When we explain what is a computed tomography scan, we are talking about a medical imaging test that combines X-rays and computer technology. It creates detailed cross-sectional images of the body, including bones, organs, blood vessels, and soft tissues. These images are much more detailed than regular X-rays.
A CT scan allows doctors to view the body layer by layer. This detailed imaging helps detect conditions that may not be visible through standard tests. The procedure is fast, painless, and highly reliable for diagnosis.
What Is The Purpose of Computed Tomography
The purpose of computed tomography is to help doctors diagnose, monitor, and sometimes guide treatment. It provides clear images that help identify injuries, infections, tumors, and internal bleeding. CT scans are also used to check how well treatments are working.
Doctors prefer CT scans because they offer speed and accuracy. In emergencies, they help identify life-threatening problems quickly. This makes them a critical tool in modern healthcare.
What Are The Uses of Computed Tomography in Healthcare
The uses of computed tomography are wide-ranging across different medical specialities. It plays an important role in diagnosing conditions early and accurately. CT scans are used for both routine checks and emergency evaluations.
Common uses include:
- Detecting fractures and internal injuries
- Identifying tumors and cysts
- Diagnosing infections and inflammation
- Evaluating heart and lung conditions
- Guiding biopsies and surgeries
Types of Computed Tomography Scans
There are several types of computed tomography scans, each designed to examine specific parts of the body. The type of scan recommended depends on symptoms and medical history. Understanding these types helps us know why a particular scan is advised.
| Type of CT Scan | Area Examined | Used To Detect |
|---|---|---|
| Head and Neck CT | Brain, skull, glands and lymph nodes | Stroke, injury, tumours, infections and bleeding |
| Brain CT | Cross-sectional images of the brain | Stroke, tumours and neurological issues |
| CT orbit scan | Eye sockets and surrounding structures | Fractures, tumours and infections |
| Chest CT | Lungs, heart and chest cavity | Infections, tumours and fluid buildup |
| HRCT Chest Scan | Lungs | Fibrosis, pneumonia and COVID-19 effects |
| Thorax CT | Lungs, oesophagus and lymph nodes | Tumour, infections and injury |
| Cardiac CT | Heart anatomy, coronary arteries | Blockages and aneurysms |
| Abdomen and Pelvis CT | Liver, kidneys, intestines and bladder | Pain, tumours, infections and digestive issues |
| Spine CT | Vertebrae, spinal canal and discs | Fractures, disc herniation and spinal injuries |
| CT KUB Scan | Kidney, ureters and bladder | Stones, blockages and infections |
| Hip Joint CT | Hip bones and joint spaces | Fractures, arthritis and joint abnormalities |
| Knee CT | Bones and soft tissues around the knee joint | Injuries, ligament damage and arthritis |
| CT Urography | Kidney, ureters and bladder | Urinary tract obstructions, stones and cancers |
Computed Tomography With Contrast Explained
Sometimes doctors recommend computed tomography with contrast for better image clarity. Contrast material is a special dye that highlights blood vessels, organs, or tissues. It makes abnormalities easier to detect.
Contrast may be given orally, through an injection, or both. Most people tolerate it well, and side effects are usually mild. Doctors always review medical history before using contrast.
How to Prepare for a CT Scan
Preparing for a CT scan is usually simple and stress-free. The preparation depends on whether contrast is used. Our team at Koshikaa provides clear instructions beforehand.
General preparation tips include:
- Informing us about allergies or medications
- Fasting for a few hours if contrast is required
- Wearing comfortable clothing without metal
- Removing jewellery before the scan
Following these steps ensures accurate results and a smooth experience.
Step-by-Step CT Scan Procedure
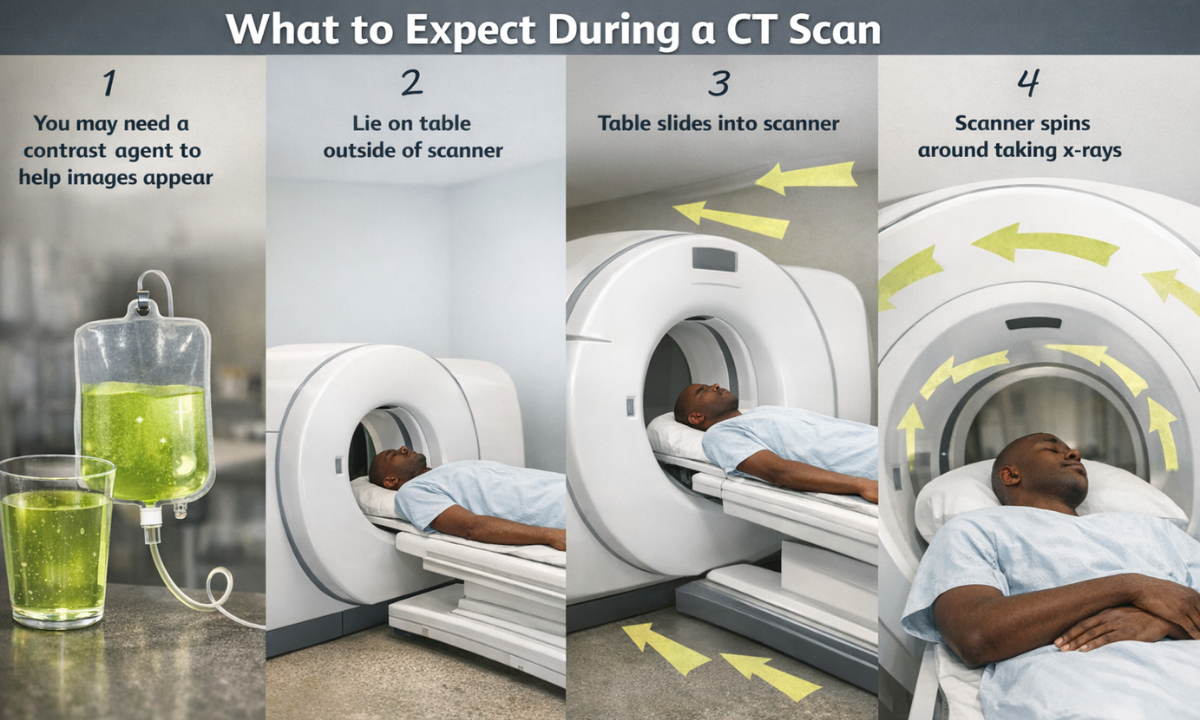
Understanding the CT scan procedure helps reduce anxiety and prepares us mentally for the test. A CT scan is a non-invasive, painless procedure that is usually completed within a short time. The entire process is conducted under the supervision of trained radiology professionals to ensure accuracy and safety.
- Before the scan begins, we are guided into the scanning room and asked to lie comfortably on a motorised table. The technician positions us carefully to ensure the correct body part is scanned. Cushions or straps may be used gently to help us stay still during the procedure.
- As the scan starts, the table slowly slides into the circular CT scanner. The scanner rotates around us, taking multiple X-ray images from different angles. These images are then processed by a computer to create detailed cross-sectional views of the body.
- During the scan, we may be asked to hold our breath for a few seconds. This helps prevent motion and ensures clear images, especially for chest or abdominal scans. We can communicate with the technician at all times through an intercom, which helps us feel reassured and supported.
- The scan itself usually takes only a few minutes, although slightly more time may be needed if contrast material is used. Once the imaging is complete, the table slides out, and we can usually return to our normal activities immediately.
At Koshikaa, patient comfort, clear instructions, and constant communication are prioritized throughout the procedure to ensure a smooth and stress-free experience.
Is a CT Scan Safe?
Safety is a common concern, and it is completely valid. CT scans do involve low levels of radiation, but they are considered safe when medically necessary. The benefits usually outweigh the risks.
Modern CT machines use advanced technology to minimize radiation exposure. Doctors recommend scans only when needed and follow strict safety guidelines.
Computed Tomography Cost: What to Expect
The computed tomography cost can vary based on several factors. These include the type of scan, use of contrast, and body area being examined. Costs may also differ between diagnostic centres.
| Factor | Impact on Cost |
|---|---|
| Type of CT scan | Basic vs advanced |
| Contrast usage | Increases cost |
| Body part scanned | Single vs multiple areas |
| Technology used | Standard vs advanced scanners |
At Koshikaa, we aim to offer transparent pricing without hidden charges. Here is the detailed cost breakdown.
| Scan | Without Contrast Cost | With Contrast Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Head and Neck CT | ₹5000/- | ₹7000/- |
| CT Brain | ₹5000/- | ₹7000/- |
| CT orbit scan | ₹4000/- | ₹4000/- |
| Chest CT | ₹6000/- | ₹6000/- |
| HRCT Chest Scan | ₹6000/- | ₹8000/- |
| Thorax CT | ₹6000/- | ₹6000/- |
| Cardiac CT | ₹6000/- | ₹6000/- |
| Abdomen and Pelvis CT | ₹6000/- | ₹12000/- |
| Spine CT | ₹6000/- | ₹8000/- |
| CT KUB Scan | ₹6000/- | ₹12000/- |
| Hip Joint CT | ₹6000/- | ₹8000/- |
| Knee CT | ₹6000/- | ₹6000/- |
| CT Urography | ₹4000/- | ₹6000/- |
Understanding a Computed Tomography Report
A computed tomography report is a detailed medical document prepared by a radiologist after carefully analysing the CT scan images. The radiologist studies each image to identify normal structures as well as any abnormalities. This report plays a key role in helping doctors confirm a diagnosis or decide the next steps in treatment.
- The report usually begins with a brief description of the scanned area and the reason the scan was performed. It also mentions the type of CT scan used, such as whether contrast material was involved. This information helps doctors understand the context of the findings.
- The main section of the report includes observations and identified abnormalities, if any. This may describe changes in organ size, shape, density, or the presence of masses, fluid, or inflammation. These findings are written in medical terms to ensure accuracy and clarity for healthcare professionals.
- Towards the end, the report provides an impression or summary. This is one of the most important sections, as it highlights the key findings and suggests possible diagnoses. In some cases, the radiologist may also include recommendations for further tests or follow-up scans.
Doctors review the CT scan report along with clinical symptoms and other test results. They then explain the findings in simple, understandable language, helping patients clearly understand their results and the planned course of care.
CT Scan for Health Screening
CT scans are sometimes used as part of preventive health screening. They help detect conditions early, even before symptoms appear. This is especially useful for high-risk individuals.
As a trusted health screening centre in Bangalore, Koshikaa focuses on responsible and need-based screening. We ensure CT scans are used appropriately and interpreted carefully. Preventive imaging can be life-saving when done correctly.
When Should We Get a CT Scan?
A CT scan is recommended when detailed imaging is needed. Doctors usually suggest it after evaluating symptoms and initial test results. It is not done routinely unless required.
Common reasons include:
- Persistent pain with unclear cause
- Suspected internal injuries
- Monitoring known medical conditions
- Evaluating treatment response
Tips for a Comfortable CT Scan Experience
A calm mindset can make the experience smoother. Simple preparation helps us feel confident and relaxed.
Helpful tips:
- Ask questions if unsure
- Follow breathing instructions carefully
- Stay still during the scan
- Inform staff about discomfort
Common Myths About CT Scans
There are many misconceptions around CT scans. Clearing them helps reduce fear and confusion.
| Myths | Facts |
|---|---|
| CT scans are extremely dangerous | Radiation levels are controlled and safe. |
| “CT scans are painful.” | The procedure is completely painless. |
| “Reports are difficult to understand.” | Doctors and centres like Koshikaa help explain results clearly. |
Final Thoughts
Understanding what is a computed tomography scan empowers us to approach medical imaging with confidence instead of fear. CT scans play a vital role in accurate diagnosis, treatment planning, and health monitoring.
At Koshikaa, we combine advanced technology with patient-first care to ensure safe and reliable imaging. If you are considering a CT scan in Bangalore, choosing a trusted diagnostic partner can make all the difference in your healthcare journey.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How does a computed tomography work?
A computed tomography scan works by using rotating X-rays and computer technology to capture multiple images from different angles. These images are combined to create detailed cross-sectional views of internal organs, bones, and tissues.
2. What is the duration of a CT scan?
The duration of a CT scan is usually short and takes about 5 to 10 minutes. Some complex scans or scans using contrast may take slightly longer, but the procedure is generally quick and painless.
3. What is the CT scan cost?
The CT scan cost depends on factors such as the body part being scanned, whether contrast is used, and the type of scan required. Costs may vary between basic and advanced CT imaging procedures. In India basic CT scan costs around ₹4000 to ₹6000, and advanced scans cost around ₹8000 to ₹12000
4. What should I inform my doctor about before a CT scan?
Before a CT scan, we should inform the doctor about allergies, kidney problems, pregnancy, ongoing medications, or previous reactions to contrast dye. This helps ensure safety and determines whether special precautions are needed.
5. Why is a CT scan done?
A CT scan is done to diagnose injuries, infections, tumors, internal bleeding, or organ problems. It helps doctors get clear and detailed images, allowing accurate diagnosis, treatment planning, and monitoring of medical conditions.
Reference:
1. https://www.nibib.nih.gov/science-education/science-topics/computed-tomography-ct
2. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diagnostics/4808-ct-computed-tomography-scan
Image source:
2. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CT_scan