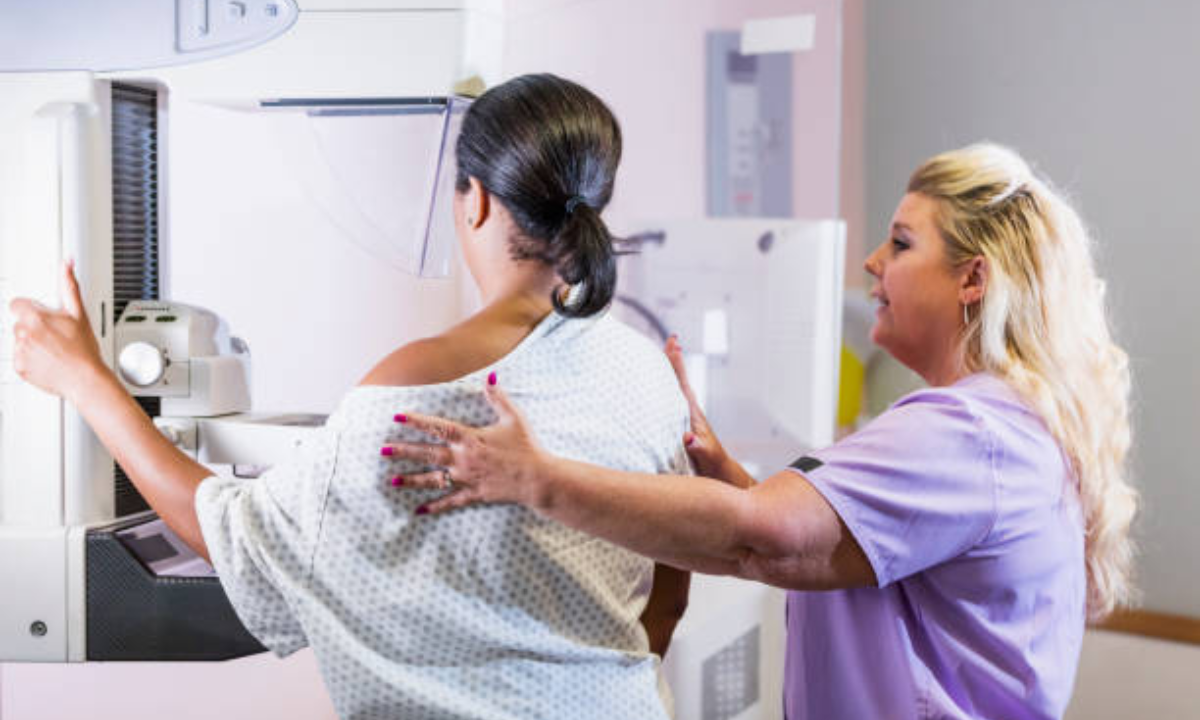
Prevention Early breast health depends on early detection. A special type of X-ray scan called a mammogram searches for changes that occur in breast tissue before you can feel them. The primary component of breast cancer screening is regular mammograms, which contribute much to treatment. This simple guide informs individuals about who should be tested, how to conduct the tests, and where to seek treatment.
Recommended Age for Mammograms
Health authorities do not coincide completely, but they share some milestones:
- The majority of recommendations suggest annual or alternate-year mammography of average-risk women beginning at age 40.
- Women normally have an option of changing every two years after age 55, provided that prior results are normal.
- Experts emphasize that every woman ought to have a personal plan – those who have dense tissue or family history can begin earlier.
- Age rules are a beginning. Effective communication between you and your provider using the shared approach can lead you to the right starting point at the right time for you.
Individual screening and risk factors
Various variables may define the time of screening:
1. Family History: 30 or 35: screening may be necessary in a first-degree relative with breast cancer.
2. Genetic Mutations: Women who have BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations undergo more vigilant monitoring.
3. History of chest treatment: Past radiation of the chest or benign breast disease should be treated with more imaging.
4. Breast Density: Breasts that are dense mask tiny tumors; there is a possibility of additional ultrasound or MRI.
When you discuss the risks with your provider, you will allow your provider to offer recommendations unique to your needs beyond age limits.
Knowledge of the mammogram test procedure

The test itself takes not so much, approximately 20 minutes:
1. A technologist places each of the breasts, one at a time, on a flat support plate.
2. The tissue is evenly spread with a second plate that produces gentle compression.
3. Each breast is typically done in two positions, i.e., top-to-bottom and side-to-side.
4. The photos are assessed at the location; subsequent glimpses can be done, where necessary.
The fact that people have some idea about the medical operation that is performed in a mammogram makes them prepared to endure mild pressure, and they understand why they might only experience little discomfort during the session.
Mammogram preparation tips
The readiness enhances comfort and facilitates the mammogram process. Here are some tips to follow:
• Take the test a week after your period is over; the breasts are not as tender.
• Do not wear deodorants, perfumes, powder, or lotions near your armpits or your breasts. Those can appear as artifacts on the images.
• Put on a two-piece top since you can undress easily in the exam room.
• If going to a new center, bring former imaging reports. A comparison of the scans provides an informative background.
• Inform personnel of implants or surgeries within the past days since it impacts the technician dealing with the application of compression and positioning.
The procedures assist in the generation of clear pictures and reduce the possibility of the need to retake the test.
Advancements in Imaging
This early detection is very important since tumors that are detected at the earliest stage are usually easy to treat and have high survival rates. Women who do not show symptoms receive an early detection mammogram in search of microcalcifications or micro masses. Instructions come in line with screening recommendations and emphasize that you repeat the examination every year or two.
Technology has been able to change film mammography to digital mammography, which transforms X-rays into high-resolution digital images. A digital mammography test is now being done in many radiology centers, which allows radiology experts to adjust the contrast and zoom in on points of interest. This increases the visibility of the lesion, particularly in dense breasts, and tends to reduce the requirement for a call back.
Accessing Services
Being in India, and a place with plenty of options (the tech capital), you are all set. Browse to the search box, put the phrase mammography in Bangalore, and browse through the credentials of the mammography provider, like the accreditation done nationally or internationally. Most hospitals in urban settings have multi-disciplinary breast units with imaging, biopsy, and oncology services co-located.
Affordable mammography in Bangalore is available in government health schemes, privately owned diagnostic chains, and community camps every now and then. Prices may differ significantly; thus, it is necessary to compare a package of charges that includes imaging, a visit to a doctor, and a follow-up report. This should prepare you so that you receive maximum care, to your surprise.
What comes after the Exam
Following the scan, the BI-RADS scale is used as a radiologist writes a report. The categories go as low as 0 (need more imaging) to as high as 6 (known cancer). The majority of screening would be BI-RADS 1 (normal) or BI-RADS 2 (benign findings), and regular follow-ups are sufficient. BI-RADS 3-6 categories frequently need additional examinations, including ultrasound, MRI, or precise biopsy. Such stages of follow-up might appear alarming, but they reduce confusion and aid in the selection of proper treatment.
Elevate Long-Term Success and Assistance
Breast health is a constant task. With your initial screening, you may set up reminders on your phone, calendar, or clinic to keep you on schedule. Conduct monthly self-checks, pay attention to changes as they happen, and combine screenings with healthy lifestyle choices to minimize the risk of developing this disease: maintain a balanced diet, lead an active lifestyle, limit the amount of alcohol consumed, and quit smoking.
Discuss risk factors, both familiar and genetic mutation, with your provider openly and bring up dense breast tissue. Request supplementary imaging consistency through ultrasound or MRI to diagnose cancer at an early age.
In addition, pay attention to the following advice:
- No deodorants, lotion, or powder on the day of the exam.
- Wear a two-piece outfit to have an easy time changing.
- The quality of communication enhances the quality of the image.
- Have routine follow-ups despite normal results.
You can have the best of both worlds with regular mammograms when combined with a healthy lifestyle. It is also important to get in touch with a support group or attend a workshop to keep track.
Question on all the steps of mammograms to be aware of the procedure.
Search to find reputable services and programmes (low-cost or free), and local health organizations and advocacy services.
Conclusion
Being aware of when you should start screening, how to go about it, and what to expect takes the control of your health into your own hands. Request your physician to schedule a mammogram and devise a regimen that is right for you. The probability of early diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer increases when healthy habits are added to the checks.
Koshikaa Screening Centre is patient-centric and well-advanced in digital technology for mammography in Bangalore. Quality exams are offered by trained technologists and board-certified radiologists. Your test will result in an online review or a telemedicine follow-up that eliminates travelling and waiting. Screening is also less costly due to financial aid and easy payment schemes.