Have you ever wondered why a simple cough that doesn’t go away can sometimes be a warning sign of something serious? Many of us ignore persistent symptoms, but understanding what tuberculosis is can help us protect ourselves and our families before complications arise.
Tuberculosis, commonly known as TB, is a contagious bacterial infection that mainly affects the lungs. It spreads through the air and can quietly grow inside the body if not detected early.
In cities like Bangalore, access to timely diagnostics, such as a CT scan in Bangalore or chest X-rays, has made early detection much easier. The key lies in awareness and acting at the right time.
Let’s explore everything you need to know about TB in a simple and practical way so that you can recognize the signs early and seek the right care without delay.
Medical Disclaimer
This blog is for general informational and educational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. If you experience symptoms such as persistent cough, fever, night sweats, or unexplained weight loss, please consult a qualified healthcare professional or visit a trusted diagnostic centre like Koshikaa for proper evaluation. Always seek medical guidance before making any health-related decisions.
Key Points At A Glance
- Tuberculosis (TB) is a contagious infection caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
- It mainly affects the lungs (pulmonary tuberculosis), but it can also affect other organs.
- TB spreads through airborne droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes.
- Common symptoms of tuberculosis include persistent cough, fever, night sweats, and weight loss.
- Early diagnosis using skin tests, blood tests, sputum tests, X-rays, or CT scans is essential.
- WHO tuberculosis guidelines stress early detection and complete treatment.
- Timely screening at a trusted health screening centre in Bangalore can prevent complications.
Understanding What Tuberculosis Is
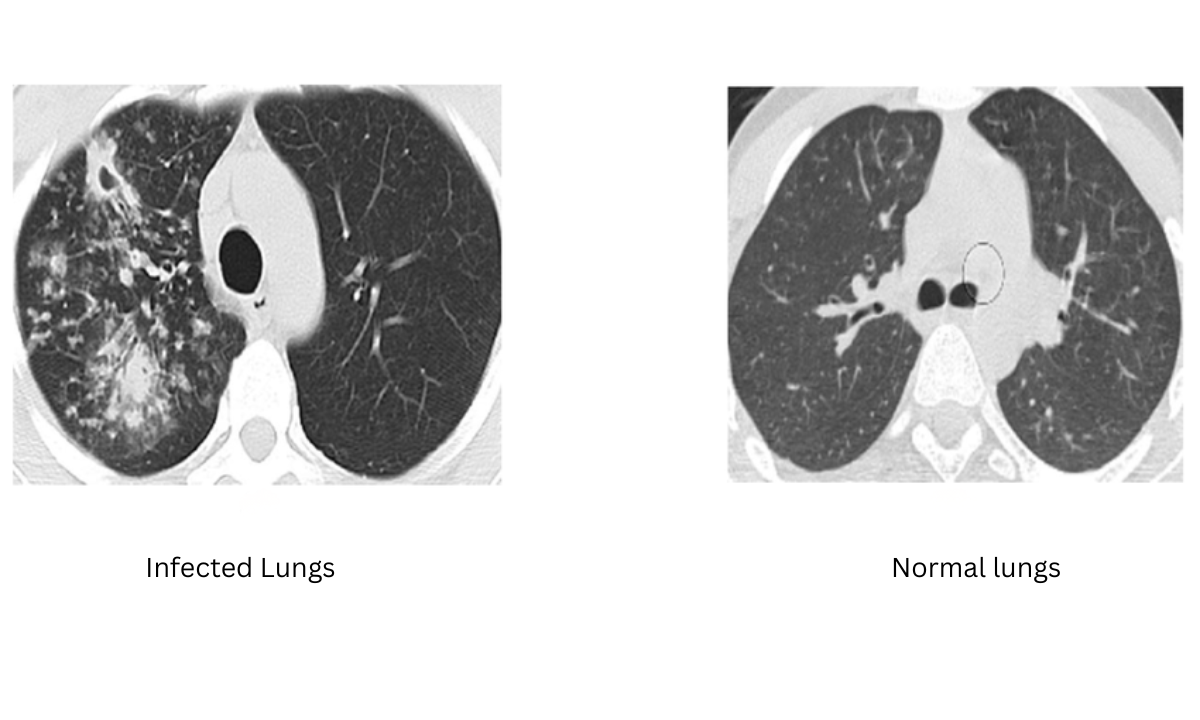
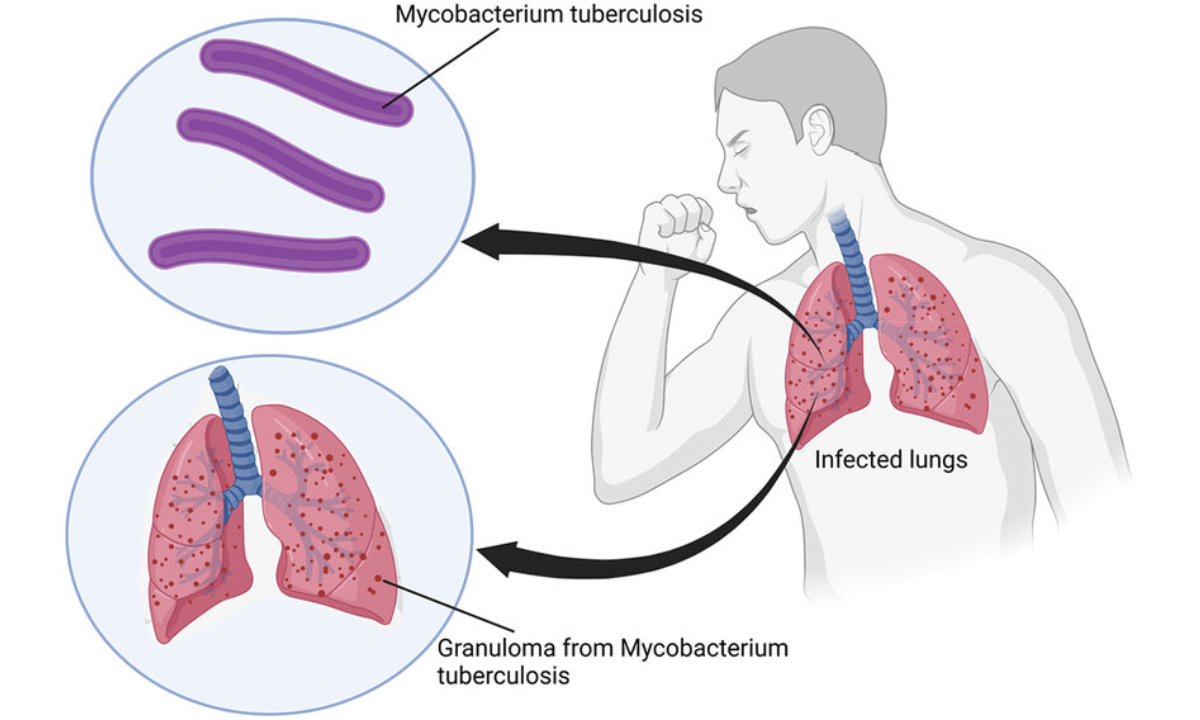
To truly understand what tuberculosis is, we must first know that it is an infectious disease caused by a specific bacterium called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It primarily attacks the lungs but can also affect other parts of the body.
When TB affects the lungs, it is called pulmonary tuberculosis. If it spreads to areas like the spine, kidneys, or brain, it is known as extrapulmonary TB.
Active TB vs Latent TB
Not everyone infected with TB bacteria becomes sick immediately. There are two forms:
| Type | What It Means | Contagious | Symptoms Present? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Latent TB | Bacteria present but inactive | No | No |
| Active TB | Bacteria are active and multiplying | Yes | Yes |
Latent TB can remain silent for years. However, it can become active if immunity weakens.
Causes Of Tuberculosis
When discussing the causes of tuberculosis, we must focus on the bacterium responsible and how it spreads.
1. Bacterial Infection
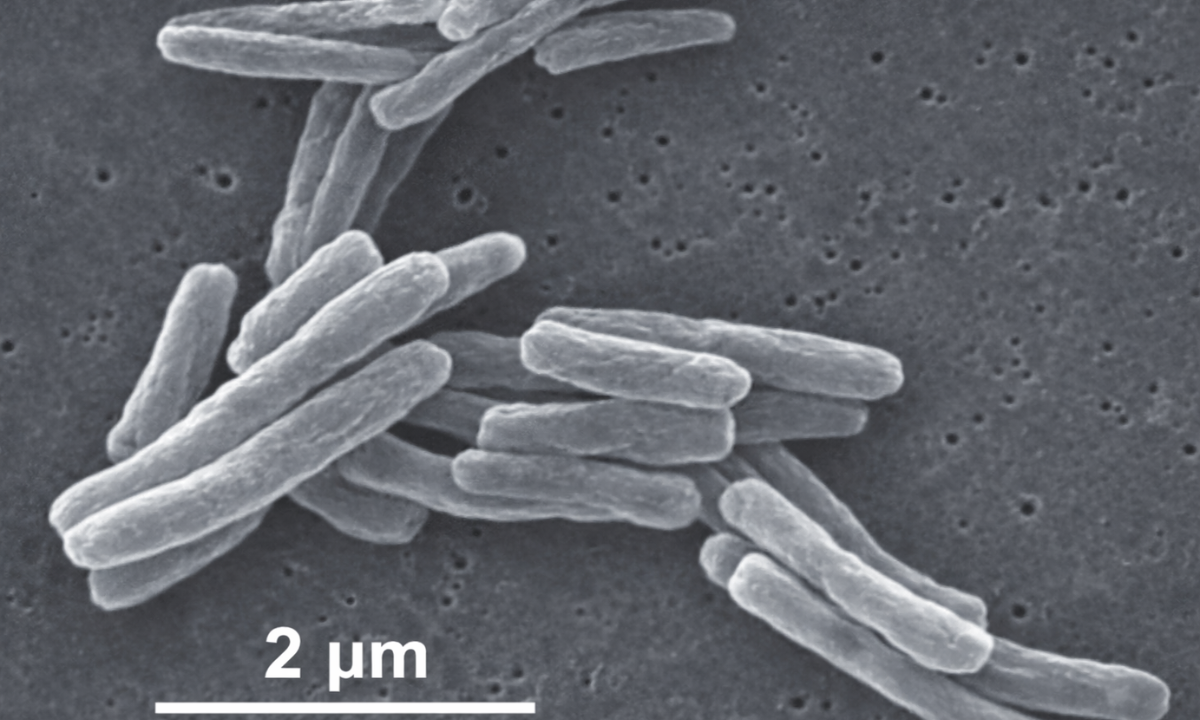
TB is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This bacterium thrives in oxygen-rich environments, which is why the lungs are most commonly affected.
2. Airborne Transmission
TB spreads through tiny droplets released into the air when a person with active pulmonary tuberculosis:
- Coughs
- Sneezes
- Speaks
- Sings
Breathing in these droplets can infect others.
3. Risk Factors
Certain conditions increase the risk of developing TB:
- Close and prolonged indoor contact with infected individuals
- Weak immune system
- Poor nutrition
- Chronic illnesses
- Living in crowded environments
We should remember that TB does not spread through handshakes, sharing food, or touching surfaces.
Pulmonary Tuberculosis Explained
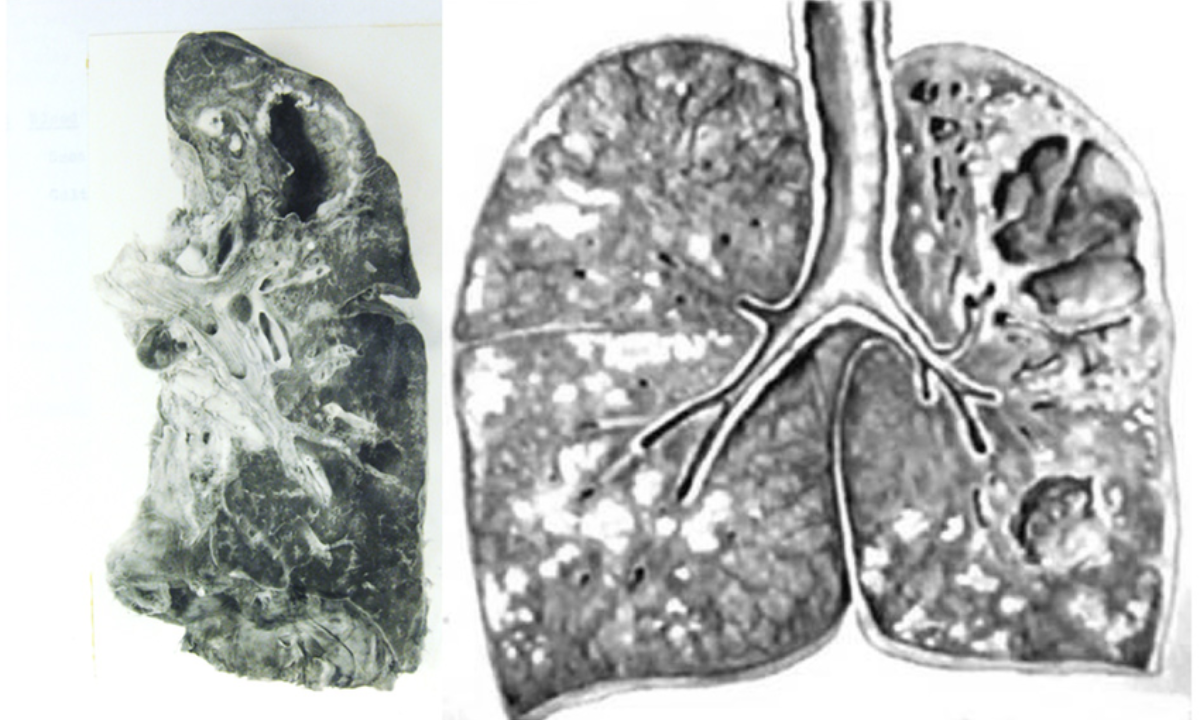
Pulmonary tuberculosis refers specifically to TB infection in the lungs. It is the most common and most contagious form.
The bacteria damage lung tissues over time. If untreated, it can cause serious breathing problems and even spread to other organs.
Example:
If someone has been coughing continuously for over three weeks with occasional blood in sputum, it may be a warning sign of pulmonary TB. Ignoring such symptoms can delay diagnosis.
Symptoms Of Tuberculosis
Recognizing the symptoms of tuberculosis early can save lives. TB symptoms often develop slowly, which makes them easy to ignore.
Common Symptoms Of Active TB
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Persistent cough | Lasts more than 3 weeks |
| Blood in sputum | Coughing up blood or mucus |
| Chest pain | Pain during breathing or coughing |
| Fever | Usually low-grade but persistent |
| Night sweats | Drenching sweats during sleep |
| Weight loss | Unexplained and gradual |
| Fatigue | Constant tiredness |
If you notice two or more of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical evaluation.
Symptoms In Extrapulmonary TB
If TB affects other organs, symptoms depend on the affected area:
- Spine: Back pain
- Brain: Headache or confusion
- Kidneys: Blood in urine
Diagnostic Test Of Tuberculosis
Early diagnosis plays a critical role in stopping TB spread. Let us understand each diagnostic test of tuberculosis clearly.
At Koshikaa, we use a combination of advanced laboratory testing and high-quality imaging to ensure accurate and timely diagnosis for every patient.
1. Mantoux Tuberculin Skin Test (TST)
A small amount of purified protein derivative (PPD) is injected under the skin. After 48–72 hours, a healthcare provider checks for swelling.
It indicates exposure to TB bacteria but does not confirm active disease.
2. TB Blood Test (IGRA)
This blood test measures the immune response to TB bacteria. It is especially useful for individuals vaccinated with BCG because it is not affected by the vaccine.
3. Sputum Test
A sputum sample from the lungs is examined under a microscope or cultured in a lab.
| Test Type | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Sputum smear | Detects bacteria under a microscope |
| Sputum culture | Confirms presence and drug sensitivity |
4. Imaging Tests
Imaging helps detect lung abnormalities.
- X ray in Bangalore facilities are widely available for quick screening.
- CT scan chest in Bangalore provides more detailed images.
A CT scan gives a clearer picture of lung damage and complications.
5. Molecular Tests (PCR)
PCR tests detect TB genetic material rapidly. They also identify drug resistance.
Role Of Imaging In TB Diagnosis
Imaging plays an important role in confirming TB, especially pulmonary tuberculosis.
| Imaging Method | When Used | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Chest X-ray | Initial evaluation | Quick and affordable |
| CT Scan | Detailed assessment | Detects early changes |
If an X-ray result is unclear, doctors may recommend a CT scan for better clarity.
Why Early Diagnosis Matters
Early diagnosis protects both the patient and the community.
Benefits Of Early Testing
- Prevents disease spread
- Reduces complications
- Ensures faster recovery
- Lowers risk of drug resistance
Visiting a trusted health screening centre in Bangalore can make testing convenient and stress-free.
WHO Tuberculosis Guidelines
The WHO tuberculosis guidelines emphasize early detection, proper treatment, and prevention.
Key recommendations include:
- Prompt diagnosis using reliable tests
- Standardised treatment regimens
- Monitoring patient progress
- Ensuring treatment completion
Incomplete treatment can lead to drug-resistant TB, which is harder to treat.
Treatment Overview
Although this blog focuses mainly on diagnosis, treatment is equally important.
TB treatment usually lasts 6–9 months and involves multiple antibiotics.
| Phase | Duration | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Intensive Phase | First 2 months | Kill most bacteria |
| Continuation Phase | Remaining months | Eliminate remaining bacteria |
Completing the full course is essential.
Practical Tips For Prevention
We can reduce TB risk with simple measures:
- Cover your mouth while coughing
- Ensure proper ventilation at home
- Avoid overcrowded indoor spaces
- Maintain good nutrition
- Get tested if symptoms persist
Early screening helps prevent complications.
When Should We See A Doctor?
We should consult a doctor if:
- Cough lasts more than 3 weeks
- There is blood in the sputum
- Fever and night sweats persist
- Sudden unexplained weight loss occurs
Ignoring symptoms may delay treatment.
Final Thoughts
Understanding what tuberculosis is gives us the power to act early and protect our health. TB is preventable, diagnosable, and treatable when we take symptoms seriously and follow medical advice.
Modern diagnostic tools, such as CT scan in Bangalore facilities and advanced laboratory testing, have made early detection more accessible than ever. Choosing a trusted healthcare provider ensures accurate diagnosis and complete care.
At Koshikaa, we focus on precise screening, reliable imaging, and patient-friendly guidance so that every individual receives a timely and accurate diagnosis.
If you or a loved one experiences persistent symptoms, do not wait. Early testing, proper guidance, and timely treatment can make all the difference in preventing complications and ensuring a healthy future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is TB curable?
Yes, tuberculosis is curable. With the correct combination of antibiotics taken regularly for the full prescribed duration, most people recover completely. Treatment usually lasts 6–9 months, and completing the entire course is extremely important to prevent recurrence or drug resistance.
2. Can latent TB become active?
Yes, latent TB can become active if the body’s immune system becomes weak. This may happen due to poor nutrition, chronic diseases like diabetes, stress, ageing, or certain medications.
When immunity drops, the inactive bacteria can multiply and cause active tuberculosis with noticeable symptoms. That is why monitoring and preventive care are important for people diagnosed with latent TB.
3. How long is TB contagious?
A person with active pulmonary tuberculosis can spread the infection to others, especially through coughing or sneezing. However, once proper treatment is started, the number of bacteria in the body gradually reduces.
In many cases, patients become much less contagious after a few weeks of consistent medication. Doctors usually monitor progress through follow-up tests to confirm that the infection is under control. Until then, precautions such as wearing masks and maintaining good ventilation are advised.
4. Do I need imaging tests for TB?
Not everyone requires advanced imaging immediately, but doctors often recommend a chest X-ray as an initial screening tool if TB is suspected. If the X-ray results are unclear or if a more detailed evaluation is needed, a CT scan may be advised.
Imaging helps detect lung damage, cavities, or infection spread that laboratory tests alone cannot fully show. It also supports treatment planning and monitoring recovery.
5. Where can I get tested?
You can get tested at a trusted diagnostic or health screening centre in Bangalore that offers TB skin tests, blood tests, sputum analysis, and imaging services under one roof.
Choosing a well-equipped centre ensures accurate reporting and expert medical guidance. Early testing is one of the most important steps in preventing complications and protecting others from infection.
Reference
1. From Google
2. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/11301-tuberculosis
Image source
1. https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Mycobacterium-tuberculosis-MBTB_fig1_380854983

