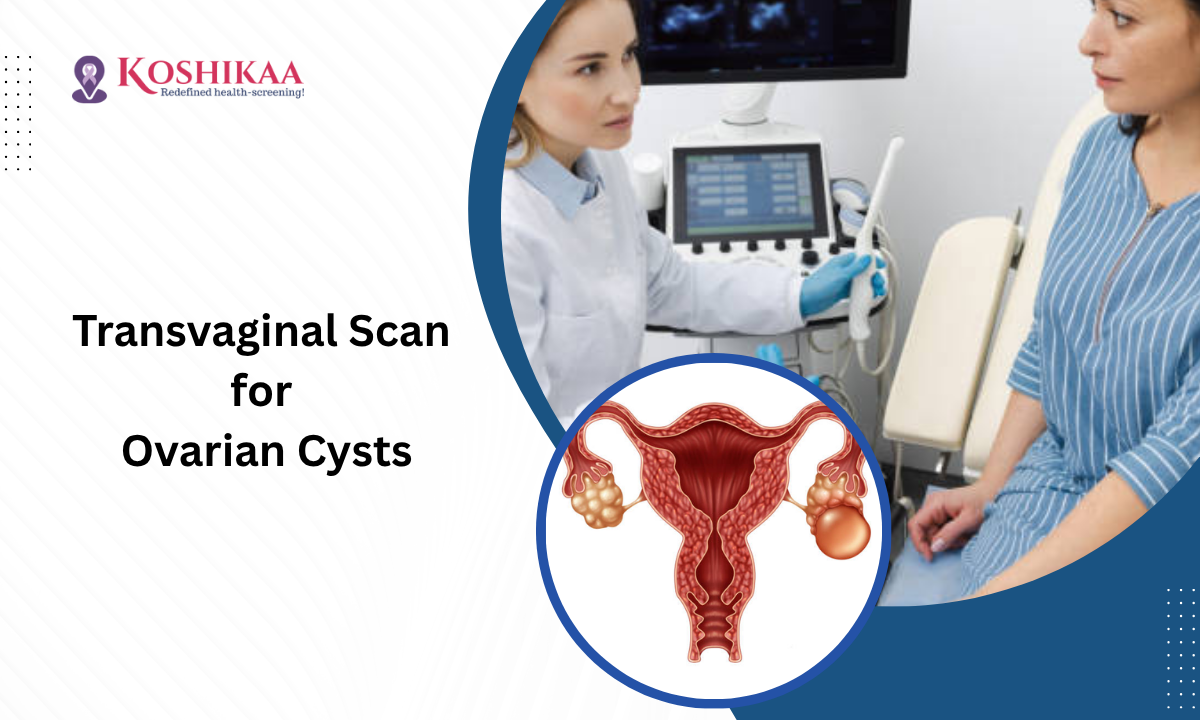
Transvaginal Ultrasound is one of the most effective tools for early detection of ovarian cysts. This non-invasive imaging technique helps doctors evaluate the ovaries, detect abnormalities, and support timely intervention for better reproductive and overall health.
Ovarian cysts can develop quietly, sometimes causing few or no symptoms initially. With a transvaginal ultrasound, you can get precise insights about your ovarian health. At our Health Screening Centre in Bangalore, we ensure that every scan is comfortable, accurate, and interpreted by experienced radiologists.
Curious about what your ultrasound might reveal about ovarian cysts and reproductive health? Keep reading to learn more.
What is a transvaginal ultrasound?
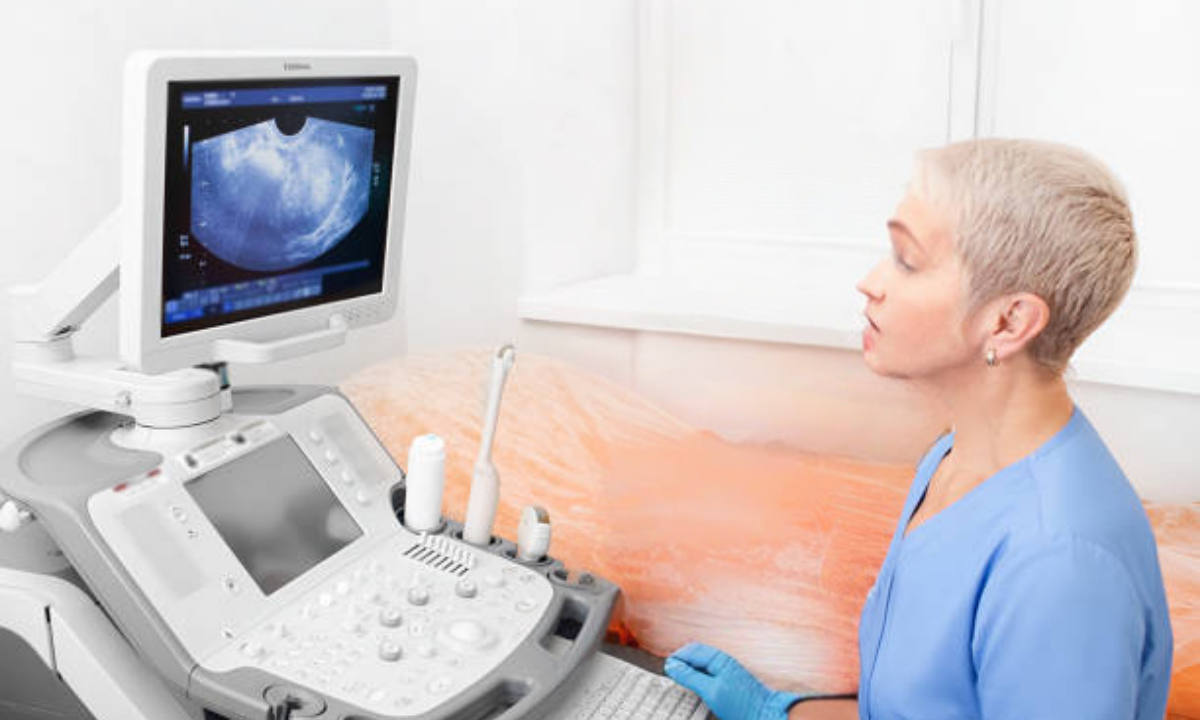
A transvaginal ultrasound uses a specially designed transvaginal probe to create high-resolution images of the ovaries, uterus, and surrounding pelvic structures.
Unlike abdominal ultrasounds, this method provides a closer and clearer view of the ovaries, making it particularly effective for detecting small cysts or early changes.
It is safe, radiation-free, and takes only about 15–20 minutes to complete.
Purpose of Transvaginal Ultrasound
A transvaginal ultrasound purpose includes:
- Detecting ovarian cysts, growths, or abnormal structures
- Evaluating uterine health and fertility-related concerns
- Guiding doctors for treatment planning or surgery if needed
- Monitoring existing ovarian cysts over time
This scan is often recommended at our Health Screening Centre in Bangalore for women with symptoms, a family history of ovarian issues, or routine reproductive health check-ups.
Understanding Ovarian Cysts
Ovarian cysts refer to fluid-filled sacs that develop in or on the ovaries. They are common in women of all ages and often disappear on their own, but some cysts may require treatment.
Ovarian cysts symptoms can include:
- Lower abdominal pain or bloating
- Irregular periods or spotting
- Pain during intercourse
- Frequent urination or pressure in the pelvic area
Many cysts are asymptomatic, which is why a transvaginal ultrasound is crucial for early detection of cancer.
How Transvaginal Ultrasound Detects Ovarian Cysts
During a transvaginal ultrasound scan, the transvaginal probe is gently inserted into the vagina. The probe emits sound waves that create real-time images of the ovaries and surrounding tissues.
Ovarian cysts in ultrasound may appear as fluid-filled sacs or complex structures, depending on their type. The scan allows doctors to:
- Identify the size, shape, and number of cysts
- Determine if cysts are simple (usually harmless) or complex (may need further evaluation)
- Track changes over time to monitor natural resolution or response to treatment
Advantages of Transvaginal Ultrasound
Some key benefits of transvaginal ultrasound include:
- Early detection: Small cysts can be identified before symptoms appear.
- Non-invasive and safe: No radiation exposure or surgical procedures required.
- Accurate imaging: Offers detailed views that abdominal scans may miss.
- Guided treatment planning: Helps in deciding whether ovarian cysts treatment is necessary.
- Comfortable and quick: Minimal preparation is needed, and results are fast.
Ovarian Cysts Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the cyst type, size, and symptoms. Common approaches include:
| Treatment Type | When Used |
|---|---|
| Watchful waiting | Small, simple cysts without symptoms |
| Medication | Hormonal therapy to prevent new cysts |
| Surgery | Large, persistent, or complex cysts |
| Fertility monitoring | When cysts affect reproductive planning |
Regular ovarian cysts ultrasound images help doctors monitor changes and decide the best approach.
Preparing for a Transvaginal Ultrasound
Preparation is simple:
- Empty your bladder before the scan for comfort.
- Wear comfortable clothing.
- Remove jewelry near the pelvic area.
- Follow any specific instructions given by your doctor or imaging centre.
No fasting is required. The scan is brief, painless, and usually well-tolerated.
Tips for Maintaining Ovarian Health
- Track menstrual cycles and note unusual symptoms.
- Maintain a healthy diet and exercise routine.
- Schedule a routine ultrasound scan in Bangalore at trusted centres.
- Consult your doctor promptly if you notice pelvic pain or irregular periods.
- Keep all past ultrasound reports for reference during follow-ups.
Routine monitoring at a health screening centre in Bangalore ensures early detection and timely care.
Key Takeaways
A transvaginal ultrasound is a reliable, safe, and effective tool for detecting ovarian cysts early. By providing accurate images, it helps in timely diagnosis and management.
Regular check-ups at a health screening centre in Bangalore can prevent complications, support fertility planning, and maintain overall reproductive health.
Monitoring ovarian cysts with ultrasound ensures that you and your doctor can make informed decisions about treatment or observation.
Final Thoughts
Your reproductive and ovarian health deserve attention even when there are no obvious symptoms. Early detection through transvaginal ultrasound empowers women to take control of their health.
At Koshikaa, we combine advanced technology, experienced radiologists, and a patient-friendly approach to deliver precise scans. If you are looking for a reliable health screening centre in Bangalore, our team is here to guide you with care, comfort, and accurate results.
Prioritize your health today, because early detection of ovarian cysts makes a significant difference in long-term wellness.
FAQs
1. What is the best ultrasound for ovarian cysts?
A transvaginal ultrasound is the most accurate for detecting small ovarian cysts, providing detailed views of the ovaries and surrounding tissues.
2. Is a transvaginal ultrasound painful?
No, it is usually painless. You may feel slight pressure during the probe insertion, but the procedure is generally comfortable.
3. How to prepare for a transvaginal ultrasound?
Empty your bladder, wear comfortable clothing, and follow any instructions from the imaging centre. No fasting or special prep is needed.
4. Can ovarian cysts affect fertility?
Some cysts may interfere with ovulation, but most resolve naturally. Regular monitoring helps manage fertility-related concerns.
5. How often should I get an ovarian cyst ultrasound?
Follow-up depends on cyst type and symptoms. Doctors may recommend scans every 6–12 months or sooner if abnormalities persist.