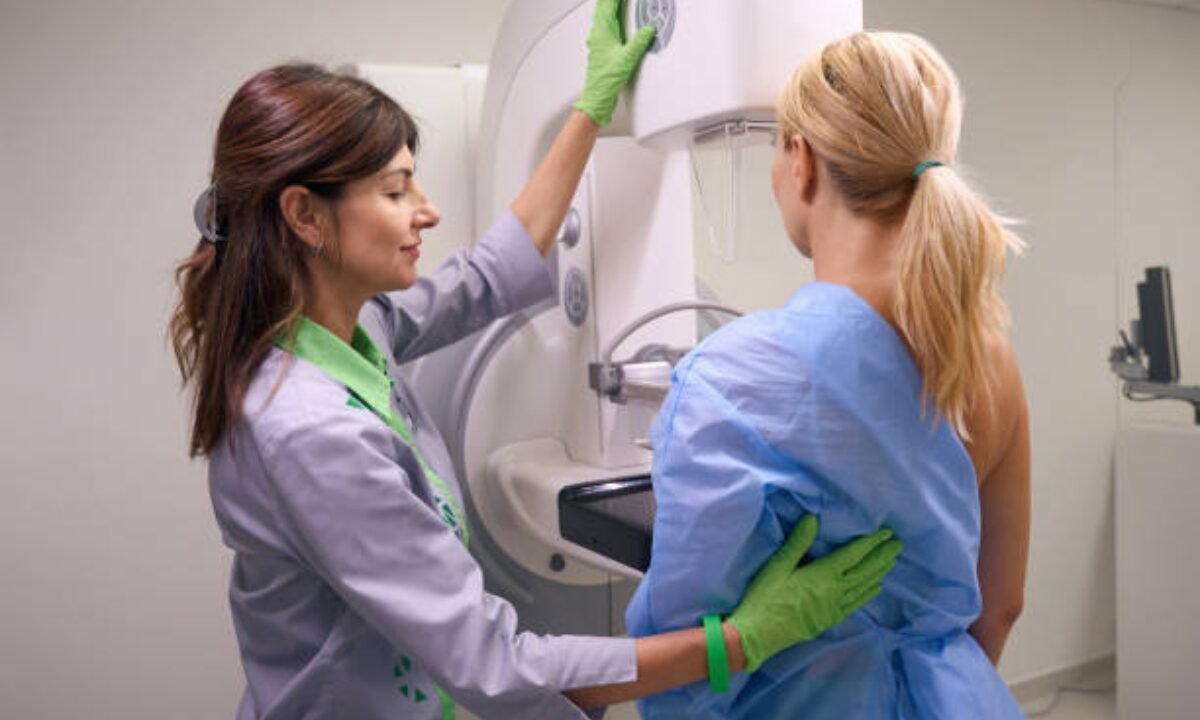
Women around the world are at risk of developing breast cancer. It is one of the most frequently diagnosed cancers and the leading cause of death from cancer in women. A mammography test is one of the most effective methods of detection in the early stage. This simple examination has prevented many breast cancers around the world in the early stages, before they become life-threatening, by finding breast cancer.
In this article, we will find out the role of regular mammography tests in treating breast cancer and why they are one of the best tools for the fight against this terrible disease.
Breast Cancer and its Challenges.
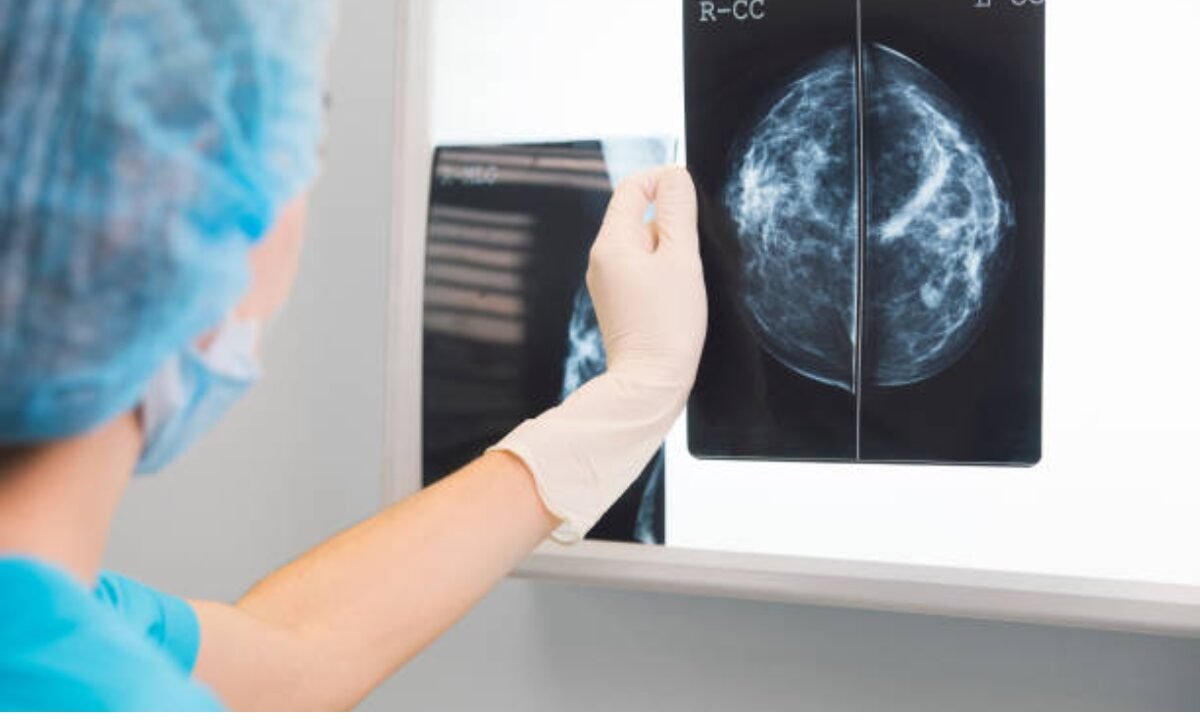
The term breast cancer can refer to a tumor that develops when cells in the breast tissue grow uncontrollably. The more cancerous cells it has, the more potential it has to spread to other areas of the body; the cancer is more difficult to treat. Successful outcomes depend greatly on early detection because the cancer is found in a stage where it is still manageable.
What is a Mammography Test?
A mammography is an X-ray performed to examine breast tissue. It is a quick, noninvasive test well suited to detect abnormalities like calcifications, cysts, or tumors of the breast. In particular, it is beneficial since the test can detect small tumors or changes in breast tissue that are not felt during a physical exam.
If you are having a mammography test, the breast is flattened into two plates to get clear X-ray images. While many women may find the procedure uncomfortable, the temporary discomfort is well worth the possible lifesaving advantages of finding cancer earlier.
Role of Mammography in Early Detection
Early detection is crucial in the treatment of breast cancer. Numerous studies and medical experts have emphasized that identifying cancer before it spreads not only improves survival rates but also enables less invasive treatment options. A mammography test can detect tumors as small as a grain of rice, well before they can be felt by hand.
In most cases, patients who catch breast cancer at its earliest stage, either stage 0 or stage 1, have a much better prognosis. Early detection by a mammography test can also reduce the necessity for aggressive treatments such as chemotherapy or mastectomy.
When Should You Have Regular Mammography Tests?
It all depends on several factors, including age, personal history of any health problems, and risk factors like family history of breast cancer. These criteria determine when and to what age the recommendations suggest you should have regular mammography tests.
1. Women above the age of 40
Doctors say women older than 40 would be wise to get screened for breast cancer every one to two years, and recommend they speak with their family doctor about what could be the best way to do so. Women in this age group are at increased risk for developing breast cancer, and regular screening can substantially decrease the incidence of late-stage disease.
2. High-Risk Individuals
Eventually, some women may start screening for early stages of breast cancer in their 30s or when their doctor orders them to do so if they have a family history or are carriers of the genetic marker BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation.
3. Post-Menopausal Women
Routine mammography tests for women are especially important especially after menopause as post-menopause breast cancer risk increases. One can detect and treat cancer on time with vigilant screening during this phase of life.
How are the Routine Mammography Tests Advantageous to you?
Indeed, the benefits of routine mammography tests include the following advantages:
1. Early Detection Saves Lives
The tests for regular mammography have been proven to reduce breast cancer death risk by finding the disease early. Early detection often means patients don’t have to suffer more painful treatments, and therefore improve their quality of life.
2. Improved Treatment Options
Unless you’re in the later stages of breast cancer, most of them can only be treated surgically or through localized radiation. The mammography test, if the cancer is caught early enough, may even save more of the breast tissue.
3. Reassurance for Women
Routine mammography exams give many women peace of mind. Once women know that the health of their breasts has been looked after and that potential problems will be spotted early, their anxiety about cancer is much diminished.
What are Mammograms and Why are they Important?
Unfortunately, however, even with the benefits, some women may be afraid or misinformed about mammography tests. The most common concerns are that they are exposed to radiation, the procedure is painful, or they do not need the test. These concerns should be addressed to encourage more women to prioritize this screening method.
1. Radiation Risks Are Minimal
The quantity of radiation in a mammography test is very low, like that which you could have from natural sources in the environment, and within a few months, it does not cause much discomfort.
2. Discomfort is Momentary.
Not everyone experiences a little bit of discomfort during the compression process. But the procedure is very short, only a few minutes. This is nothing compared to the potential benefits.
3. Not all abnormalities are cancer.
Also, know that regardless of an abnormal mammography result, it doesn’t always mean cancer. Unfortunately, the result in actuality, is often benign, or it is not cancerous in most instances.
Mammography with Other Screening Tools
A mammography test is a good, but far from perfect, way to detect breast cancer early. In some cases, specifically in women with dense breast tissue some further imaging, such as ultrasound or MRI, may be needed to confirm findings. And self-examination and regular clinical breast exams are also part of a woman’s total breast health program.
Instead of working against a one-size-fits-all healthcare approach, the goal is to proactively combat the risk of breast cancer by working with healthcare providers to create a personalized screening plan that may include regular mammography tests.
What is the Future of Mammography Tests?
Technology continues to advance mammography tests becoming more effective. Our innovations such as 3D mammography — also known as tomosynthesis — provide more detailed images of the breast so that smaller tumors can be detected, particularly in women with dense breast tissue. The future offers greater accuracy and fewer false positives.
Conclusion
Regular mammography tests are an invaluable assistance in the fight against breast cancer. When they detect the disease early, they give women better treatment options, better chances of survival, and a greater chance of being cured. Mammograms are a tool to empower women to take control over their breast health, and by doing so encourage women to return yearly and become proactive when they need to be.
There is no one-size-fits-all all, but healthcare providers suggest screening in a personalized fashion for each woman based on unique risk factors. Performing mammography can save lives, and the simple act of one does so much to catch breast cancer early. Mammograms are proof that preventive care is powerful.
At Koshikaa we offer state-of-the-art facilities for mammography in Bangalore to diagnose breast abnormalities accurately and at an early stage, facilitating the treatment.