Imagine your heart is a house. For the plumbing (blood vessels) to work, the wiring (electricity) must be perfect.
Every single time your heart beats—about 100,000 times a day—it is triggered by a tiny electrical impulse.
This invisible spark tells your heart muscle to squeeze and pump blood to the rest of your body.
But what happens if the wiring goes faulty? What if the spark is too weak, too fast, or coming from the wrong place? This is where the Electrocardiogram comes in.
You might have seen it in movies: the beeping machine with the green zigzag lines. But in real life, this simple test is the first line of defense against heart disease.
Whether you are experiencing sudden chest pain or just going for a routine check-up, understanding what an electrocardiogram test is can take the fear out of the process.
In this guide, we will decode the ECG test full form in medical terms, explain how it works without a single needle prick, and show you why it is the gold standard for cardiac screening.
What is an ECG Test?
So, what exactly is an ECG Test? The ECG test in medical terminology is an Electrocardiogram.
- Electro: Related to electricity.
- Cardio: Related to the heart.
- Gram: A record or drawing.
Put simply, an ECG is a recording of the electrical activity of your heart over a period of time.
Think of it like an electrician using a voltmeter to check if a circuit is working. The ECG machine places sensors on your skin to “listen” to the electrical signals traveling through your heart.
It then translates these silent signals into a visual graph (waves) on paper or a screen.
Why is it called an EKG sometimes? You might hear doctors use “ECG” and “EKG” interchangeably. They are the same test. “EKG” comes from the German spelling (Elektrokardiogramm).
How Does it Work?
Capturing the heartbeat, beat by beat.
To understand the ECG test result, you need to know that your heart is an electrical pump.
- The Spark: It starts at the top of your heart (SA Node), sending a wave of electricity down to the bottom chambers.
- The Squeeze: This wave causes the muscle to contract and push blood out.
- The Reset: The heart then “recharges” for a split second before the next beat.
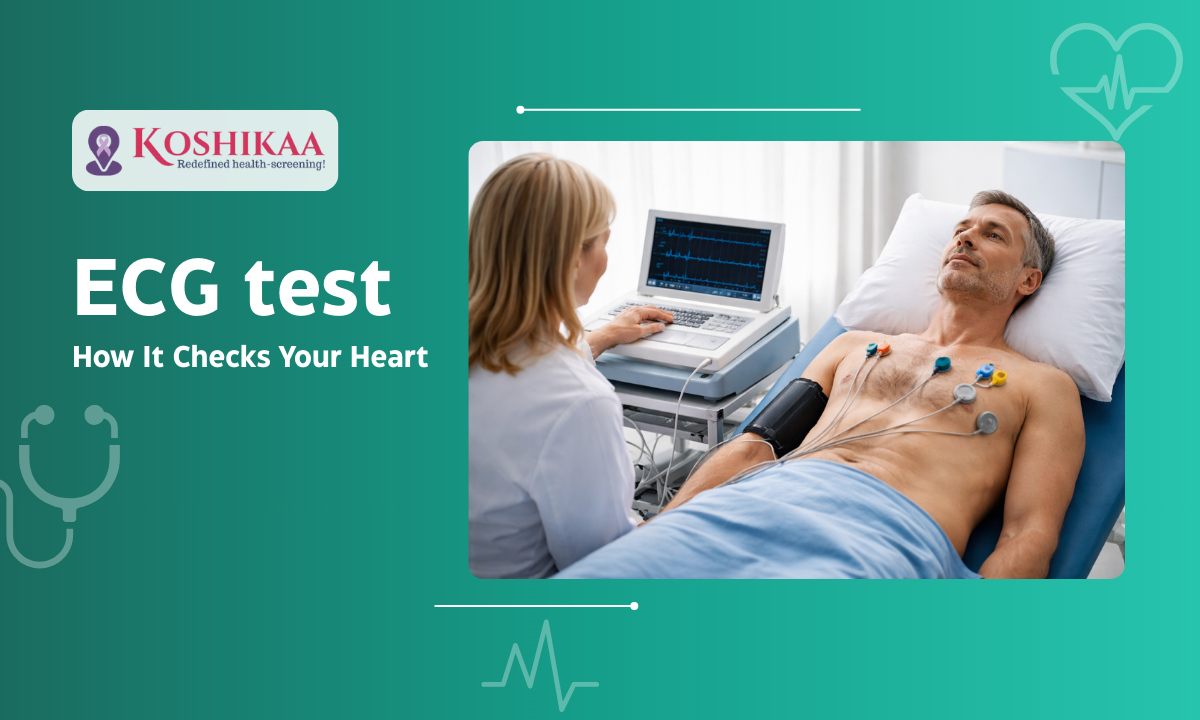
The ECG machine uses small sensors (electrodes) placed on your chest, arms, and legs.
Think of these electrodes as cameras taking pictures of your heart’s electricity from 12 different angles (which is why it’s often called a 12-lead ECG).
It combines these “pictures” to draw a continuous line graph.
- The P-Wave: The spark starting at the top.
- The QRS Complex: The big spike when the main chambers pump.
- The T-Wave: The heart recharging/relaxing.
If there is a blockage or damage, electricity can’t travel smoothly. The line on the graph will look distorted—like a stutter in the signal.
Why Would a Doctor Prescribe It?
It’s not just for heart attacks.
Many people assume an ECG is only for emergencies. However, for a Health screening centre in Bangalore, it is a vital preventive tool.
Your doctor might ask for an ECG for two reasons: specific symptoms or hidden risk factors.
When Should You Get an ECG?
| If You Feel These Symptoms… | If You Have These Risk Factors… |
|---|---|
| Palpitations: Feeling like your heart is racing, fluttering, or skipping a beat. | High Blood Pressure: Long-term pressure can thicken the heart muscle (Hypertrophy). |
| High Blood Pressure: Long-term pressure can thicken the heart muscle (Hypertrophy). | Diabetes: Diabetics often have “silent” heart issues with no obvious pain. |
| Shortness of Breath: Getting winded easily after climbing just one flight of stairs. | Family History: If a parent or sibling had heart trouble before age 55. |
| Dizziness/Fainting: This suggests the heart might be beating too slowly (Bradycardia). | High Cholesterol: Clogged arteries change how electricity flows through the heart. |
Koshikaa Insight: In Bangalore, we see many young IT professionals with ‘Palpitations’ due to high caffeine and stress. An ECG is the quickest way to confirm that your heart structure is normal and that the racing heart is just lifestyle-induced, not a defect.
The Procedure: 10 Minutes, Zero Pain
No needles. No shocks. Just stickers.
If you are nervous about medical tests, here is the good news: An ECG is one of the safest, least invasive procedures in medicine.
Unlike a blood test, there are no needles. Unlike an MRI, there are no loud noises or tight spaces.
How to Prepare
Preparation is minimal, but a few small things ensure a clear reading:
- No Body Lotions/Oils: This is crucial. Oil creates a barrier on your skin that makes it hard for the sensors (electrodes) to stick or read the electrical signal. Do not apply moisturizer to your chest or arms on the day of the test.
- Clothing: Wear a shirt or blouse that can be easily unbuttoned or removed. You will need to expose your chest for the sensor placement.
- No Fasting Needed: You can eat and drink normally before an ECG.
The Step-by-Step Experience
Whether you visit a Health screening centre in Bangalore or book a home service, the steps are identical:
- The Setup: You will be asked to lie down flat on a bed or examination table. Relaxing is important because shivering or muscle tension can create “noise” on the graph.
- The Stickers: The technician will place about 10 small, sticky patches (electrodes) on your body:
- 6 on your chest (across the heart area).
- 4 on your limbs (wrists and ankles).
- Note: For men with hairy chests, a small patch might need to be shaved to ensure the sticker makes contact with the skin.
- The Recording: The technician presses a button. The machine records your heart’s activity for about 10 to 30 seconds. You simply lie still and breathe normally. You will feel absolutely nothing—no electricity enters your body; the machine only reads what is coming out.
- The Result: The stickers are removed (like a band-aid), and the machine prints out the graph or sends it digitally to a cardiologist.
If you are getting an ECG test in Bangalore clinics, bring your previous ECG reports if you have them.
A ‘normal’ ECG looks different for everyone. Comparing the new graph with the old one helps the doctor spot changes, which is often more important than the graph itself.
Decoding the Result: What Do the Lines Mean?
Reading the language of your heart.
When you get your report, you will see a lot of squiggly lines and some technical terms. While only a doctor should interpret the final diagnosis, it helps to understand the basic vocabulary.
Common Terms You Might See on an ECG Report
| Term on Report | What it Means | Is it Serious? |
|---|---|---|
| Normal Sinus Rhythm | Good News. Your heart is beating at a normal speed (60–100 beats/min) and in a regular pattern. | No. This is the goal. |
| Tachycardia | Your heart is beating too fast (>100 bpm). | Could be due to stress, fever, or exercise. Needs checking if you were resting. |
| Bradycardia | Your heart is beating too slowly (<60 bpm). | Common in athletes. Can be an issue if you feel dizzy or faint. |
| Arrhythmia | The rhythm is “irregular.” The beats are not evenly spaced. | Requires a doctor’s review to see if it’s harmless or needs medication. |
| Ischemia | Poor blood flow. The heart muscle isn’t getting enough oxygen. | Yes. This often indicates a blockage or risk of a heart attack. |
Convenience & Cost: Why Step Out?
High-quality diagnostics without the traffic.
Bangalore is known for two things: great weather and terrible traffic.
For a simple 10-minute test, spending 2 hours in traffic to reach a hospital doesn’t make sense—especially if you are feeling unwell or accompanying an elderly parent.
This is why ECG test at home in Bangalore services have surged in popularity.
- How it works: A trained technician arrives on a bike with a portable, FDA-approved ECG machine (the size of a laptop).
- The Quality: Portable machines today are just as accurate as the bulky hospital ones for standard screening.
- The Comfort: You lie on your own bed. This naturally lowers your heart rate and stress, often leading to a more accurate “resting” reading.
Cost of ECG Test in India
One of the best things about the ECG is its affordability. It is one of the cheapest cardiac safety nets available.
| Service Type | Estimated Cost (Bangalore) | Pros/Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Local Diagnostic Lab | ₹300 – ₹500 | Cheapest, but requires travel and waiting time. |
| Hospital / ER | ₹600 – ₹1,000+ | Fast results, but higher “facility charges.” |
| Home ECG Service | ₹800 – ₹1,200 | Highest Convenience. Ideal for seniors or busy professionals. |
Why Choose Koshikaa? We combine the Health screening centre in Bangalore quality with home convenience. Our technicians don’t just hand you a graph; our reports are reviewed by qualified doctors to ensure no subtle warning sign is missed.
Conclusion
Your heart works tirelessly, beating 100,000 times a day without a break. The least we can do is give it 10 minutes of attention once a year.
An Electrocardiogram is not just a test for the sick; it is a reassurance for the healthy. It is the simplest, fastest, and most affordable way to know that your body’s “engine” is running smoothly. Whether you are a busy professional ignoring that mild chest heaviness or a senior citizen due for a routine check, don’t wait for an emergency to prioritize your heart.
With Koshikaa, you don’t need to brave the Bangalore traffic to find answers. Our ECG services in Bangalore bring the clinic to your living room, ensuring that professional care is just a doorbell away.
Don’t skip a beat. Book your home ECG today.