Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scans are an important tool in modern healthcare because they provide doctors with extremely detailed images of the body that can help them detect a variety of illnesses. MRI, unlike other imaging techniques such as X-rays or CT scans, generates images using powerful magnets and radio waves rather than harmful radiation. This makes it a popular choice among both patients and doctors. Whether you’re preparing for an MRI scan in Bangalore or simply want to learn more about the procedure, knowing what an MRI entails will help you relax and gain clarity.
In this comprehensive tutorial, we will cover all you need to know about MRI scans, including how they work, the benefits, and any potential issues. If you are a patient undergoing an MRI scan, a caregiver assisting a loved one through the process, or a medical enthusiast, this article will walk you through each step of the procedure, explain how to prepare, and discuss what to expect during and after the scan, including how it contributes to accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
What Is an MRI Scan?

An MRI scan is a non-invasive imaging technology that gives clinicians detailed views of the body’s internal structures without using radiation. Instead of employing X-rays or other forms of radiation, MRI creates highly detailed images of soft tissues such as the brain, muscles, joints, and internal organs. This makes MRI particularly valuable for diagnosing and monitoring a wide range of medical conditions, including neurological and musculoskeletal disorders. The clarity and precision of MRI imaging enable clinicians to uncover anomalies that might otherwise go undetected.
Patients in Bangalore can have an MRI scan at a variety of hospitals and screening centers. These scans are crucial in understanding complex health conditions, allowing clinicians to make accurate diagnoses and therapy recommendations. Whether you experience joint pain, headaches, or other inexplicable symptoms, an MRI scan can help you find the source and get the right therapy.
How Do MRI Scans Work?
MRI scans employ magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the body’s internal systems. Here’s a brief description of the procedure:
Magnetic Field: The MRI equipment generates a strong magnetic field that briefly aligns the hydrogen atoms in your body. Hydrogen is plentiful in fluids and soft tissues, making it necessary for producing clear images.
Radio Waves: Radio waves are created when hydrogen atoms align. They move throughout your body. These waves interact with aligned atoms, causing them to produce weak signals.
Signal Collection: A computer gathers and interprets the transmitted signals to produce high-resolution, cross-sectional images of your organs and tissues.
Image Creation: The images produced provide a comprehensive view of the inside structures, allowing clinicians to discover anomalies, diagnose various disorders, and follow the efficacy of therapy.
Types of MRI Scans
MRI scans are classified into several categories, each of which is designed to evaluate certain parts of the body and address different medical concerns:
Brain MRI: This sort of scan is used to assess the brain for tumors, strokes, aneurysms, and other neurological problems. It generates detailed images that can be used to diagnose and monitor brain abnormalities.
Spinal MRI: This scan focuses on the spine and can reveal disorders such as herniated discs, spinal cord damage, or other spinal abnormalities. It’s critical for identifying back discomfort and other problems.
Musculoskeletal MRI: This scan looks at muscles, tendons, and ligaments to detect injuries or disorders like arthritis. It’s very useful for evaluating athletic injuries and joint disorders.
Cardiac MRI: This scan is used to assess the anatomy and function of the heart and can aid in the diagnosis of a variety of heart illnesses, including congenital heart abnormalities and cardiomyopathy.
Abdominal MRI: This scan produces detailed images of the abdominal organs, such as the liver, kidneys, and pancreas, allowing doctors to diagnose problems affecting these areas.
Benefits and Risks of MRI Scan:
Benefits:
Non-Invasive: Because MRI scans are non-invasive and painless, they are a safe imaging method that does not require surgery.
No radiation: Unlike X-rays and CT scans, MRI does not use ionizing radiation. This makes it a safer choice for routine imaging, particularly for children and pregnant women.
Detailed Imaging: MRI produces extremely detailed images of soft tissues such as the brain, muscles, and organs, which are critical for precise diagnosis and treatment planning.
Versatility: MRI scans can diagnose a wide range of problems, including neurological disorders, joint injuries, heart disease, and gastrointestinal concerns.
Risks:
Claustrophobia: The enclosed MRI equipment may cause some individuals to experience anxiety or claustrophobia. For these individuals, sedation or open MRI equipment may be recommended.
Magnetic Fields: The MRI machine’s intense magnetic field could injure persons who have metal implants, pacemakers, or other electrical equipment. It is critical to notify medical staff about any such device.
Contrast Dye: A contrast agent (dye) may be employed to improve image clarity. While it is uncommon, some people may have allergic reactions to the contrast dye; consequently, you must advise your healthcare practitioner of any known sensitivities.
MRI Scans Cost and Availability
The cost of an MRI scan varies greatly based on the type of scan, facility, and location. While these factors influence the price, it’s worth noting that MRI scans are frequently covered by insurance if judged medically essential. Before booking your scan, contact your insurance provider to ensure coverage and explain any potential out-of-pocket costs.
MRI scans are generally available in hospitals, diagnostic clinics, and speciality imaging facilities. However, the availability and wait periods for an MRI vary depending on your location and the severity of your medical condition. In some circumstances, urgent scans may be scheduled more quickly, although routine scans may require lengthier wait times. To ensure a seamless process, work with your healthcare practitioner and the imaging center to schedule the most convenient appointment time and location for you.
Preparation for an MRI Scan
Preparing for an MRI scan is a simple process, but there are a few crucial steps to ensure everything goes smoothly:
Remove Metal Objects: Any metal items, such as jewelry, watches, or piercings, must be removed before your MRI scan. Metal can interfere with the magnetic field of an MRI machine, thus it must be removed to prevent issues during the scan.
Wear Comfortable Clothing: Choose loose, comfortable clothing with no metal components. In rare cases, you may be asked to wear a medical gown provided by the imaging center to ensure that no metal objects interfere with the scan.
Medication: Inform your doctor about any medications you’re currently taking. Generally, you can continue your medication as prescribed unless your doctor advises otherwise.
Fasting: For certain MRI scans, such as those of the abdomen, you may need to fast for several hours beforehand. Be sure to follow any fasting instructions given to you.
Contrast Dye: If your MRI involves a contrast agent, you’ll be asked about any allergies or past reactions to contrast materials to ensure your safety.
What to Expect During an MRI Scan
MRI scans typically take 30-60 minutes, depending on the type of scan. Here’s what you may expect:
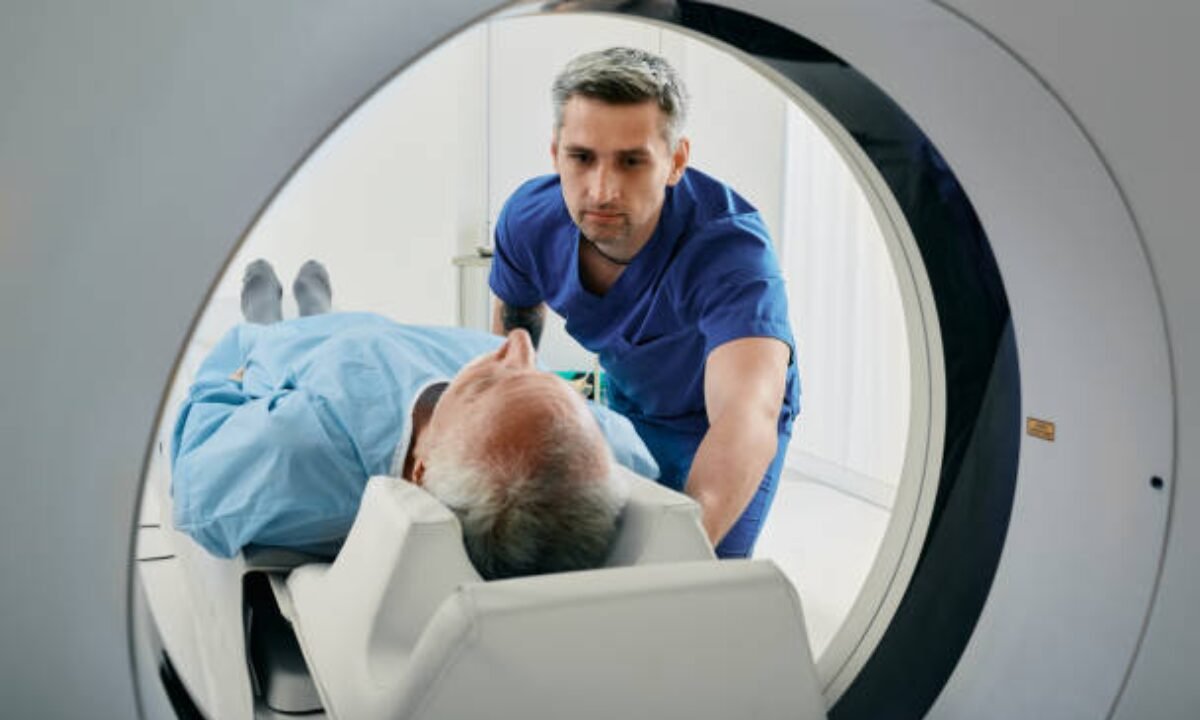
Positioning: You will lie on a motorized table that slips smoothly into the MRI machine. The MRI machine is a large tube-shaped device that contains a powerful magnet.
Immobility: To get clear, precise images, you must remain perfectly still throughout the scan. The machine will make loud, rhythmic noises throughout the operation, but you will be provided earplugs or headphones to alleviate the noise and discomfort.
Communication: During the scan, you can converse with the MRI technician via an intercom system. If you are experiencing any discomfort or need assistance, please contact the technician right away. They’ll be able to respond swiftly to ensure your comfort and resolve any issues.
Risks and Safety Considerations of MRI Scans
While MRI scans are generally viewed as safe, there are some important safety concerns to consider:
Metal Implants: Tell your doctor if you have any metal implants, such as pacemakers, cochlear implants, or metal joints. An MRI’s powerful magnetic field may interact with these gadgets, so your doctor should be aware to ensure your safety.
Pregnancy: While MRI is generally considered safe for pregnant women, see your doctor if you are or suspect you are pregnant. This enables them to assess the importance of the scan and any potential hazards.
Claustrophobia: If you have a fear of confined areas (claustrophobia), inform your doctor ahead. They may prescribe a small sedative to help you feel more at ease and relaxed during the scan, resulting in a smoother encounter.
Conclusion: The role of MRI scans in diagnosis and treatment.
MRI scans are effective diagnostic tools for a wide range of medical diseases, including neurological and musculoskeletal issues. They provide detailed images to assist clinicians in developing suitable treatment plans, monitoring the efficacy of ongoing treatments, and making educated decisions about your care. Although the MRI technique may appear terrifying at first, knowing what to expect will help ease your fears and make the session more comfortable.
If you’re preparing for an MRI, remember that it’s a safe and necessary part of your healthcare journey. MRI scans in Bangalore are critical for assessing your health and guiding your treatment since they give clear, detailed images. With proper preparation and understanding of the technique, you can go into the scan with confidence, knowing that it will contribute significantly to your total medical care.
Koshikaa Screening Centre offers a wide range of comprehensive cancer screening services, ensuring accurate results and personalized health care. Contact us today at +91 7996666104