MRI for the brain and spine is one of the most powerful tools doctors use to detect neurological and spinal conditions. It gives highly detailed images without using harmful radiation, making it both safe and effective.
In this blog, we will explain what an MRI is, its uses and procedure, and why it’s so crucial. Stay with us as we uncover how this scan reveals what other tests often miss.
What is an MRI Scan of the Brain and Spine?
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) uses strong magnets and radio waves to produce clear pictures of internal organs and tissues. Unlike X-rays or CT scans, MRI doesn’t use radiation, making it safer for long-term monitoring.
| Aspect | MRI for the Head | MRI Spine Test |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Brain, nerves, and surrounding tissues | Spinal cord, discs, and vertebrae |
| What it Shows | Tumours, strokes, nerve disorders | Back injuries, nerve compression, and deformities |
| Advantage | Non-invasive, highly accurate for neurological issues | Non-invasive, highly accurate for spinal conditions |
Why is MRI Recommended for Brain and Spine?

An MRI can reveal problems at an early stage, which is vital for treatment planning. For example, a tumor detected early with an MRI for brain cancer can often be treated with better outcomes, and spinal nerve compression identified on time can prevent permanent damage.
Thus, MRI serves as both a diagnostic and monitoring tool, guiding doctors to design personalized treatment plans.
MRI Procedure for Brain and Spine
The MRI procedure is straightforward, safe, and usually completed within 30–60 minutes.
Step-by-step process:
- Preparation: Patients remove all metal items. If contrast is required, fasting may be advised.
- Positioning: You lie on a cushioned table that slides into the MRI machine.
- Scanning: The scanner makes loud tapping sounds, but earplugs or headphones are provided.
- Completion: After the scan, you can resume your normal routine.
With Contrast vs Without Contrast
- MRI head with contrast CPT code: A special dye is injected to highlight blood vessels or detect small tumors.
- MRI head without contrast: A general scan without dye, sufficient for many neurological and spine conditions.
The choice depends on the condition being investigated.
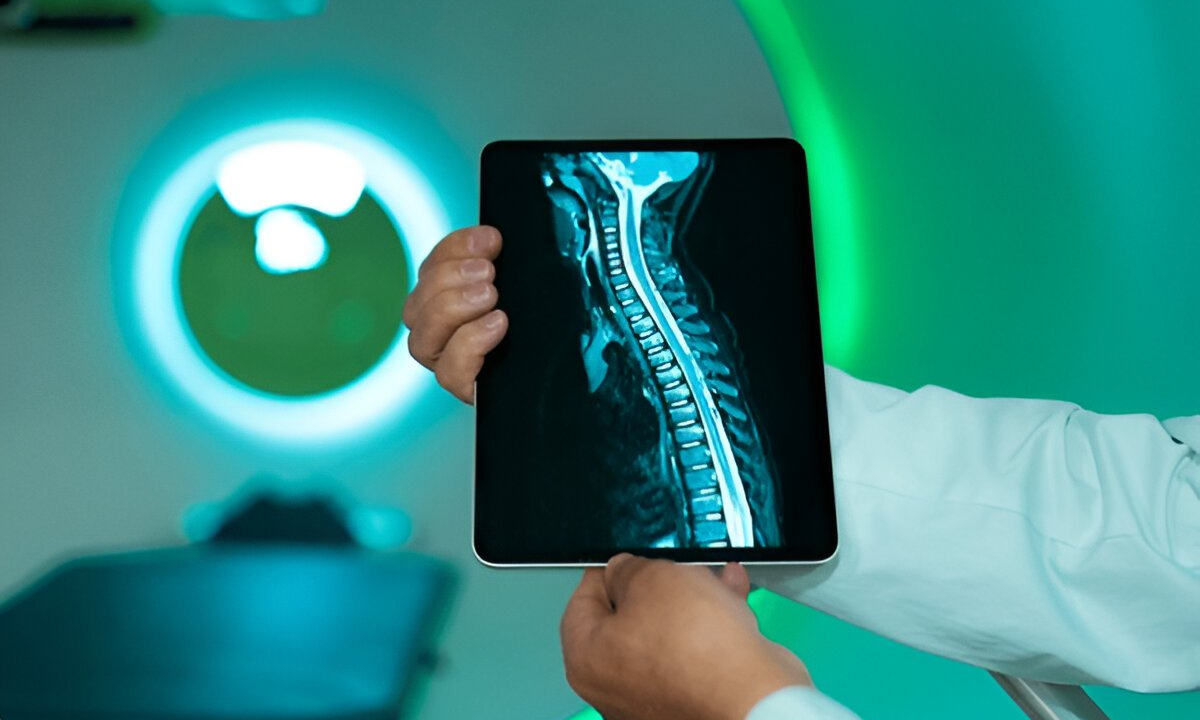
MRI Head and Spine Images
MRI head images and MRI spine images reveal critical details such as nerve pathways, blood vessels, and tissue abnormalities.
A normal brain MRI shows well-defined brain structures, while abnormalities like tumors or strokes appear as bright or dark spots. Similarly, spine MRIs can reveal slipped discs, fractures, or inflammation.
However, interpretation must always be done by a trained radiologist who can connect the findings to the patient’s symptoms and history.
MRI for Back Problems
For patients with back problems, MRI is the most reliable tool to detect herniated discs, scoliosis, or nerve compression. It shows detailed cross-sections of the spine that X-rays cannot.
When it comes to the brain, MRI is indispensable in diagnosing migraines, multiple sclerosis, trauma, and brain cancer.
In complex cases where symptoms overlap, a combined brain and spine MRI helps doctors trace the root cause, whether it originates in the nervous system or the spinal cord.
MRI Scan in Bangalore
Patients seeking an MRI Scan in Bangalore have access to advanced technology and skilled radiologists. Leading centres provide fast reports and comfortable experiences, reducing patient anxiety.
Choosing the right facility ensures both accuracy and timely results. Look for centres that offer modern MRI machines, experienced staff, and comprehensive health screening services.
Final Thoughts
The MRI for the brain and spine is a safe, non-invasive, and highly effective way to detect conditions early and plan treatments. Its precision makes it a vital tool in modern healthcare.
If you are considering an MRI scan in Bangalore, consulting a trusted health screening centre like Koshikaa ensures reliable diagnosis, accurate reports, and peace of mind.
FAQs on MRI for Brain and Spine
1. What is an MRI Scan of the Brain and Spine?
It is a non-invasive imaging test that uses magnets and radio waves to capture detailed brain and spine images, helping doctors diagnose neurological and spinal conditions.
2. Can a Brain and Spine MRI be done at the same time?
Yes, both can be scanned in a single sitting, especially in cases where neurological and spinal symptoms overlap.
3. How long does a full spine and brain MRI take?
It usually takes 60–90 minutes, depending on whether contrast is used.
4. Is MRI better than CT for brain and spine scans?
Yes. While CT scans are faster and useful for emergencies, MRI provides more detailed images of the brain and spinal cord, especially for soft tissue conditions.
5. Are there any risks with brain and spine MRI?
MRI is very safe since it does not use radiation. However, patients with metal implants, pacemakers, or severe claustrophobia should inform their doctor beforehand.