We have all seen this happen: A diabetic patient has a doctor’s appointment on Friday. So, starting Monday, they stop eating sweets, skip the rice, and go for long walks.
On Friday morning, their Fasting Blood Sugar result looks perfect.
The doctor smiles, the patient smiles. But deep down, the body knows the truth.
This is the problem with standard blood sugar tests. They are like a Snapshot—they only capture a single moment in time. If your sugar was high yesterday but low today, the snapshot misses it.
The HbA1c test is different. Think of it as a CCTV Camera for your blood. It doesn’t just look at today; it records the average sugar levels of the last 3 months.
It captures every laddoo, every skipped meal, and every stress spike.
For anyone living with diabetes (or trying to prevent it), this test is the ultimate “Truth Serum.” In this guide, we will explore the reason for the hba1c test, how to read those confusing percentages, and where to find a reliable Health Screening Centre in Bangalore to get it done.
Let’s decode the story your blood has been trying to tell you.
What is HbA1c?
Most people just call it the “Sugar Test,” but the name HbA1c is actually a precise code.
To understand what is happening in your body, we need to decode this acronym letter by letter.
Decoding the Acronym
According to clinical biochemistry standards (and the separation methods used to discover it), here is what the name actually stands for:
- Hb = Hemoglobin: This is the protein inside your Red Blood Cells that carries oxygen.
- A = Adult: This specifies the type of hemoglobin. Adults have “Type A” hemoglobin (Babies have Type F).
- 1 = The Fraction: When scientists separate blood components in a lab (chromatography), this specific group separates first.
- c = The Sub-type: This is the most important part. The “1” group has three parts (a, b, and c). The “c” part is the specific spot where glucose chemically bonds to the N-terminal valine of the beta chain.
In simple English: HbA1c is the specific “Adult” oxygen-carrying protein that has been chemically bonded with sugar at a precise molecular spot.
Now that you know the name, here is the mechanism. Imagine your Red Blood Cells are Glazed Donuts.
Your Red Blood Cells float in your bloodstream (which is like a syrup of sugar and water).
If the sugar level is high, the excess glucose starts sticking to the Hemoglobin. This process is called Glycation.
Once sugar sticks to the cell, it stays there forever. It cannot be washed off.
This is the HbA1c glucose attachment diagram for you to understand the difference between the raw cell and sugar attached cell.
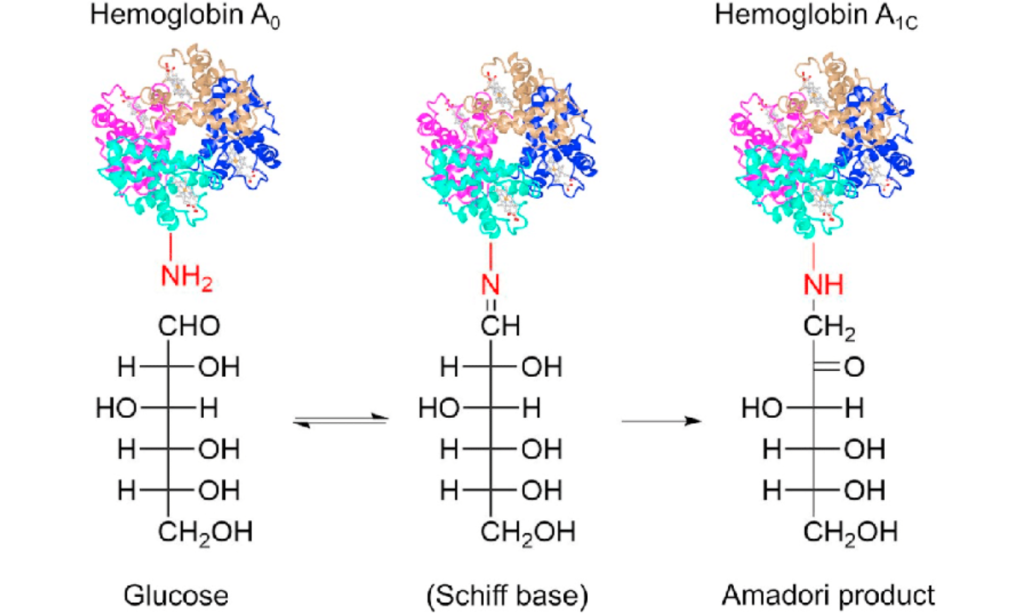
Image source: ResearchGate.
Why Exactly 3 Months?
You might wonder, “Why not 1 month or 6 months?” The answer lies in the life of a Red Blood Cell.
A Red Blood Cell lives for exactly 120 Days (approx. 3-4 months).
After that, your spleen destroys the old cell and your bone marrow makes a new, fresh one.
Therefore, the HbA1c test measures the “sugar coating” on all the cells currently alive in your body—which represents the average of the last 90 days.
While it covers 3 months, the test is slightly biased toward the recent past.
50% of your result comes from the last 30 days. 50% comes from the 2 months before that.
Which means, If you have been strictly disciplined for the last 4 weeks, your results will show improvement!
Decoding Your Report
Your report will have a percentage number. Here is exactly what it means for your health.
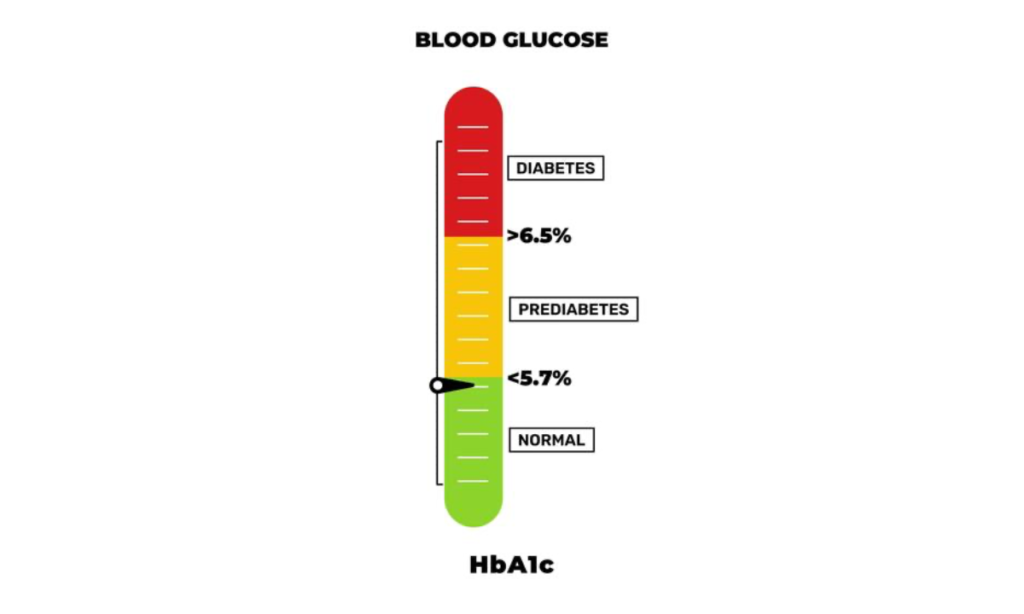
We categorize your HbA1c levels into three distinct zones. Think of it like a traffic signal.
| Zone | HbA1c Level | What it Means | The Action Plan |
|---|---|---|---|
| GREEN | Below 5.7% | Normal | You are safe. Your sugar metabolism is working perfectly. Continue your healthy lifestyle. |
| YELLOW | 5.7% – 6.4% | Pre-Diabetes | The Warning Zone. You do not have diabetes yet, but you are on the edge. This is 100% reversible with diet and exercise. |
| RED | 6.5% or Higher | Diabetes | The Danger Zone. Your average sugar has been consistently high. You need immediate medical consultation to prevent organ damage. |
Here is a visual representation for you to understand your sugar levels in a chart format:
Converting % to mg/dL
Most people know their sugar number (e.g., 140 or 180), but they don’t understand “7%”. Use this table to convert your HbA1c % into your Estimated Average Glucose (eAG).
| If your HbA1c is… | Your Average Sugar (last 3 months) was approx… |
|---|---|
| 5% | 97 mg/dL |
| 6% | 126 mg/dL |
| 7% | 154 mg/dL (Target for Diabetics) |
| 8% | 183 mg/dL (High) |
| 9% | 212 mg/dL (Critical) |
| 10% | 240 mg/dL (Dangerous) |
| 12% | 298 mg/dL (Hospitalization Risk) |
If your HbA1c is 7%, it means your sugar stays around 154 mg/dL most of the time. For most diabetic patients, doctors aim to keep the HbA1c below 7% to prevent damage to eyes and kidneys.
Book your Blood test in bengaluru today.
HbA1c vs. Random Blood Sugar: The Rivalry
A common question we hear at Koshikaa is: “If I check my sugar at home with a glucometer, why do I need to pay for a lab test?”
To answer this, we need to understand the difference between Weather and Climate.
- Random Blood Sugar (Glucometer) is like the Weather. It changes every hour. It tells you if it is raining right now.
- HbA1c is like the Climate. It tells you if the whole season was rainy or dry.
Comparison Table: Which Test Wins?
| Feature | Random Blood Sugar (RBS) | HbA1c Test |
|---|---|---|
| What it measures | Glucose floating in blood at this exact second. | Glucose stuck to cells over the last 3 months. |
| Affected by | The laddoo you ate 1 hour ago, stress, or a recent workout. | Long-term lifestyle, chronic diet habits. |
| Can you “cheat”? | YES. Skip dinner, and your morning sugar looks low. | NO. You cannot hide 3 months of history. |
| Best used for | Emergency checks (e.g., feeling dizzy/low sugar). | Diagnosing Diabetes & monitoring long-term health. |
| Accuracy | High fluctuation (Variable). | Highly Stable (Gold Standard). |
The Confusing Scenarios, Why results might not match:
Sometimes, your home kit says one thing, and the lab report says another. Here is why.
Scenario 1: “My home sugar is Normal, but HbA1c is High.”
- The Cause: This is the classic Spike Misser.
- Your sugar might be normal in the morning (fasting) but spikes dangerously high after lunch or dinner. Since you only test in the morning, you miss the spikes. But the HbA1c captures them all.
Scenario 2: “My home sugar is High, but HbA1c is Normal.”
- The Cause: This is often the Stress Spike.
- Maybe you were stressed, sick, or had a heavy meal just before the test. This caused a temporary jump, but your overall 3-month control is actually good.
Dr. Tip: Never rely on just one. Use Random Sugar to decide what to eat today. Use HbA1c to decide your medication dosage for the next 3 months.
Do I Need to Starve for the HbA1c Test?
This is the most common question we get at our Health Screening Centre in Bangalore: “Can I have my morning coffee before the test?”
The short answer is: YES.
The Fasting Rule: Zero Hours.
Unlike the “Fasting Blood Sugar” test which demands 8–10 hours of hunger, the HbA1c test requires NO fasting.
- You can eat.
- You can drink water, tea, or coffee.
- You can take your regular medicines.
The sugar attached to your Hemoglobin is stuck there from the last 3 months.
Even if you eat a chocolate bar right before the test, it will only spike the free-floating sugar in your blood.
It won’t have time to stick to the Red Blood Cells instantly. Therefore, your HbA1c score remains unchanged.
While HbA1c itself doesn’t need fasting, please check your package.
If you are booking a Full Body Checkup that includes HbA1c plus other tests, the rules might change:
| Test Combination | Fasting Required? | Why? |
|---|---|---|
| Only HbA1c | NO | You can book it for 2 PM after lunch if you want. |
| HbA1c + Fasting Sugar | YES (8-10 Hours) | The Fasting Sugar part requires an empty stomach. |
| HbA1c + Lipid Profile | YES (10-12 Hours) | Lipid (Cholesterol) tests are sensitive to food. |
If you are busy and hate morning queues, book a “HbA1c Only” test. You can schedule a Blood Test Sample Collection at Home in Bengaluru during your lunch break or evening tea time.
HbA1c Test Cost in Bangalore
Prices for the same test can vary from ₹300 to ₹1200 depending on the lab’s “brand tax.”
At Koshikaa, we believe in transparent, NABL-certified testing without the hidden costs.
Here is the 2026 market breakdown for HbA1c test cost in Bangalore.
| Provider Type | Estimated Cost (Bangalore) | Report Time | Is Home Collection Free? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Big Hospital Labs | ₹600 – ₹900 | 12 – 24 Hours | No (Usually Requires Visit) |
| Local Small Labs | ₹250 – ₹400 | Varies | Often No |
| Koshikaa (Standalone) | ₹299 | 6 Hours | YES (In select packages) |
| Koshikaa (Home Visit) | ₹349 | 6 Hours | Included |
Instead of paying ₹349 for just one test, check Koshikaa’s Basic Health Checkup package. For just ₹1,099, you often get HbA1c + Thyroid + Lipid + Liver + Kidney tests together. It’s better value for money.
Why Book a Blood Test in Bengaluru at Home?
Bangalore traffic is bad. Your health shouldn’t suffer because of it.
Booking a Blood Test Sample Collection at Home in Bengaluru is not just about laziness; it’s about Accuracy.
- Stress-Free Samples: Traveling in traffic raises cortisol (stress hormone), which can slightly alter blood parameters. Testing at home keeps you calm.
- Safety: No waiting in crowded waiting rooms with other sick patients.
- Speed: Koshikaa’s phlebotomists cover the entire city, ensuring your sample reaches our NABL-certified lab within minutes, not hours.
How to Book in 3 Steps:
- Select: Choose “HbA1c” or a “Diabetes Package” on the Koshikaa website/app.
- Slot: Pick a time (e.g., 7:00 AM before work).
- Relax: Our vaccinated expert arrives, collects the sample painlessly, and you get the report by teatime.
Conclusion
Managing diabetes without an HbA1c test is like driving a car with a broken speedometer—you might feel fine, but you have no idea how fast you are actually going.
The reason for the HbA1c test is simple: It is your 3-month truth serum.
It tells you if your current lifestyle is working or if it needs a tweak.
Whether you are in the “Green Zone” or fighting to get out of the “Red Zone,” the first step to control is accurate measurement.
At Koshikaa, we understand that a blood test is more than just a transaction; it is a health milestone. As a trusted Health Screening Centre in Bangalore, we ensure that your samples are handled with clinical precision and your reports are delivered with speed.
Don’t wait for symptoms to show up. Book your Blood test in Bengaluru today, get your Detailed HbA1c Report, and take back control of your health.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: How often should I get the HbA1c test done?
- If you are Diabetic: Every 3 months. (Since red blood cells renew every 3-4 months, testing sooner won’t show significant changes).
- If you are Pre-Diabetic: Every 6 months to monitor progress.
- If you are Healthy: Once a year as part of your annual health screening.
Q2: Can stress affect my HbA1c results?
Indirectly, YES. While a single stressful day won’t change the number, chronic long-term stress releases hormones like cortisol, which keeps your blood sugar consistently high. If you have been stressed for months, your HbA1c will likely be higher.
Q3: Can I reverse a high HbA1c score?
YES. Pre-diabetes (5.7% – 6.4%) is 100% reversible. Even Type 2 Diabetes (6.5%+) can often be put into “remission” (brought back to normal range) with significant weight loss, diet changes, and exercise. It takes about 3 months of discipline to see the number drop.
Q4: Is the HbA1c test safe for pregnant women?
Yes, but it is not the primary test. Doctors usually prefer the OGTT (Oral Glucose Tolerance Test) for pregnancy because blood volume changes during pregnancy can make HbA1c slightly less accurate. Always follow your gynecologist’s specific advice.
Q5: Why is my HbA1c high if I don’t eat sweets?
Sugar isn’t just in sweets. Rice, wheat (roti), bread, and potatoes are all carbohydrates that turn into glucose (sugar) in your blood. If your diet is heavy in carbs—even if it’s “salty” food—your HbA1c can still spike.

