Welcome to our dedicated guide on CT angiography for the heart—an advanced imaging method that lets us, as clinicians at Koshikaa, look inside your heart’s blood vessels in a non-invasive way. If you’ve ever wondered how doctors check for blockages or narrowing in the arteries supplying the heart, this procedure offers clarity and precision. We’ll walk you through why this test is done, how it’s performed, what images and data it produces, and what you need to know about risks and benefits. Let’s get started.
What Is CT Angiography for the Heart?
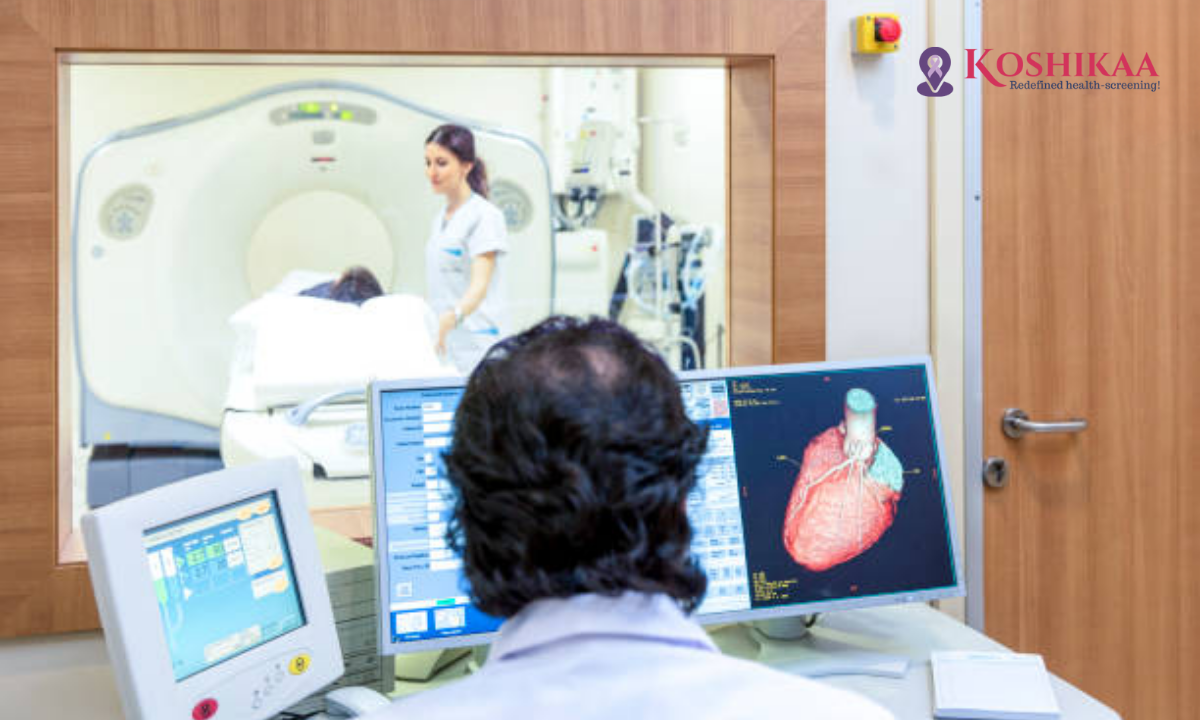
CT angiography is a specialized form of computed tomography (CT) that uses contrast dye and X-rays to create detailed three-dimensional images of the heart’s arteries and blood vessels. With this scan, we can visualize the coronary arteries—the vessels supplying your heart muscle—to spot plaque buildup, narrowing (stenosis), or other abnormalities.
In short, when we refer to CT angiography for the heart, we mean using CT scan technology to image cardiac blood vessels, helping with diagnosis, treatment planning, and monitoring of heart-related conditions.
CT Angiography – Indications (When It Is Done)
There are several reasons why we may recommend CT angiography. In this context, you may also see that CT angiography is done for various conditions, especially related to the heart. Here are common indications:
- Suspected coronary artery disease (CAD) due to chest pain, shortness of breath, or other symptoms.
- Inconclusive or borderline results from other tests, such as stress tests or echocardiograms.
- Assessment of the coronary arteries before heart interventions such as bypass surgery or stenting.
- Follow-up of previously diagnosed heart disease or grafts to check patency.
- Evaluating congenital heart abnormalities or anomalies in the arteries of the heart.
- Sometimes, when evaluating other vessel systems like the lungs (see CT angiography pulmonary, but relevant when heart and lung interaction is suspected.
By applying CT angiography in the cardiac context, we gain insights into artery narrowing, plaque, and blood-flow impairments that affect heart health.
CT Angiography Procedure – What to Expect
When we perform the CT angiography procedure for the heart, here’s a step-by-step overview from preparation to completion. You’ll see the role of things like the contrast dye, heart rate control, and image acquisition.
Preparation:
- You’ll usually be asked to fast (no food) for a few hours before the scan, and avoid caffeinated drinks because caffeine elevates heart rate, which can blur images.
- We’ll review your medications, kidney function (especially if you have known kidney disease), and any allergies (particularly to contrast dye).
- In some cases, we may give you medicine (for example, a beta-blocker) to slow your heart rate, making the imaging clearer.
During the Procedure:
- You’ll lie on the CT scanner table, and we’ll attach electrodes to your chest to monitor your heart rhythm.
- A small IV line is placed (usually in your arm) to inject the contrast dye—this enhances the blood vessels’ visibility.
- The table moves through the CT machine, and you’ll be asked to hold your breath for short intervals to minimise motion.
- The actual image capture of the heart may take as little as a few seconds, though overall, you might spend 30-60 minutes depending on preparations.
- When the scan is complete, you’re free to leave after appropriate monitoring.
After the Scan:
- Drink plenty of fluids to help flush out the contrast dye from your body.
- You can typically resume normal activities soon afterwards unless instructed otherwise.
- The images will be reviewed by us and discussed with you, including any findings and next steps.
In our centre, we take steps to make this process smooth and comfortable, ensuring you are informed and relaxed.
CT Angiography Heart Images – What We See
The images generated by CT angiography allow us to visualize the heart and its arteries in 3D, which gives much more detail than standard X-rays. We can look for:
- Blockages or narrowing in the coronary arteries.
- Plaque buildup (fatty, calcified) in the vessel walls.
- Structural abnormalities of the heart’s blood vessels.
- Assessment of bypass grafts or stents to confirm patency.
- In cases where lung circulation is involved, we might also see changes relevant to CT angiography pulmonary studies (e.g., checking pulmonary arteries for clots, though that’s a separate indication).
These images help us decide whether invasive procedures are needed or whether lifestyle and medical therapy might suffice.
CT Angiography – Procedure Time
One of the advantages of CT angiography is that it is relatively quick. The actual scan—the moment when the imaging is done—may last just a few seconds. However, the full procedure time, including preparation, possible medications to slow heart rate, contrast injection, monitoring, and image review, may amount to 30 minutes to one hour.
In some settings, if additional medications are needed or if heart rate control is more complex, the total time may stretch closer to an hour. But compared to traditional catheter-based angiography, this is considerably faster and more comfortable.
CT Angiography Risks and Benefits
As with any medical test, we weigh the benefits and risks before recommending CT angiography.
Benefits:
- Non-invasive compared to catheter angiography (no arterial catheter insertion).
- High-resolution images of the coronary arteries.
- Rapid acquisition and results that can expedite decision-making.
- Excellent “rule-out” test: if the arteries appear normal, it gives us confidence that major coronary disease is unlikely.
- Helps plan interventions or guide treatment strategies.
Risks:
- Exposure to ionising radiation (though modern CT scanners and protocols minimize this).
- Use of contrast dye: potential for allergic reactions (rare) and risk in patients with impaired kidney function.
- In some cases, the test may detect incidental findings of uncertain significance, causing anxiety or further testing.
- With heart rate or arrhythmia issues, image quality may suffer, potentially requiring repeat scanning or alternative tests.
We take all these into account, discuss them with you, and ensure the procedure is safe and appropriate.
CT Angiography Pulmonary – A Brief Note
While our focus here is on heart imaging, it’s worth mentioning that CT angiography can also be used to image pulmonary arteries—often referred to as CT angiography pulmonary. That test is primarily done to detect pulmonary embolisms (blood clots in the lungs). In our practice at Koshikaa, if you have symptoms involving both heart and lung circulation, we may coordinate and interpret findings in the context of both the heart and pulmonary vascular systems.
CT Scan in Bangalore – Why Choose a Specialist Centre
If you are looking for a CT scan in Bangalore, especially for heart-related imaging, choosing a dedicated centre makes a significant difference. At our Health Screening Centre in Bangalore, we ensure:
- Advanced CT scanners with cardiac gating and low-dose radiation protocols.
- Expertise in cardiovascular imaging and a supportive team that coordinates clinical consultation.
- Comfortable patient experience, clear preparation instructions, and prompt reporting.
- Integration with broader health screening: if we detect heart risk factors during CT angiography, we can link to preventive medicine, lifestyle counselling, and follow-up studies.
When selecting a centre, check for cardiac imaging accreditation, experience in cardiac CT angiography, and strong patient care support.
Final Thoughts
At Koshikaa, we believe that understanding your heart should never involve guesswork. That is why we offer CT angiography for the heart as part of our comprehensive cardiovascular imaging services. This test empowers us to look inside your coronary arteries with clarity—detecting narrowing, plaque, or structural anomalies, often before symptoms become severe. With proper preparation, modern equipment, and experienced clinicians, the procedure is safe, swift, and insightful.
As with any medical decision, we balance the risks and benefits, explain why the test is indicated, and tailor our approach to your health context. If you are seeking a high-quality CT scan in Bangalore, particularly in a setting where heart imaging and overall health screening go hand in hand at a leading Health Screening Centre in Bangalore, we’re here for you.
We invite you to speak with us about whether CT angiography is right for your situation and plan the next steps together.
FAQs
Q: What does “CT angiography is done for” mean in a heart context?
A: It means we use the test to find out if your heart’s blood vessels are narrowed, blocked, or have plaque that may affect your heart health.
Q: How long does the CT angiography procedure take?
A: While the scan itself may take only seconds, the full appointment, including preparation and monitoring, usually takes about 30 to 60 minutes.
Q: Are there any risks related to CT angiography of the heart?
A: Yes. There is exposure to radiation and use of contrast dye, which may cause allergic reactions or affect the kidneys in susceptible individuals. We take all precautions.
Q: Can CT angiography also check for pulmonary artery issues?
A: Yes. Although distinct, the principle of CT angiography can be applied to pulmonary arteries (CT angiography pulmonary) when we need to assess lung circulation or clots.
Q: Why choose a Health Screening Centre in Bangalore for a CT scan rather than a general imaging centre?
A: A dedicated centre provides specialized cardiac imaging protocols, expert interpretation, and a coordinated screening approach. This enhances accuracy, comfort, and overall care.

