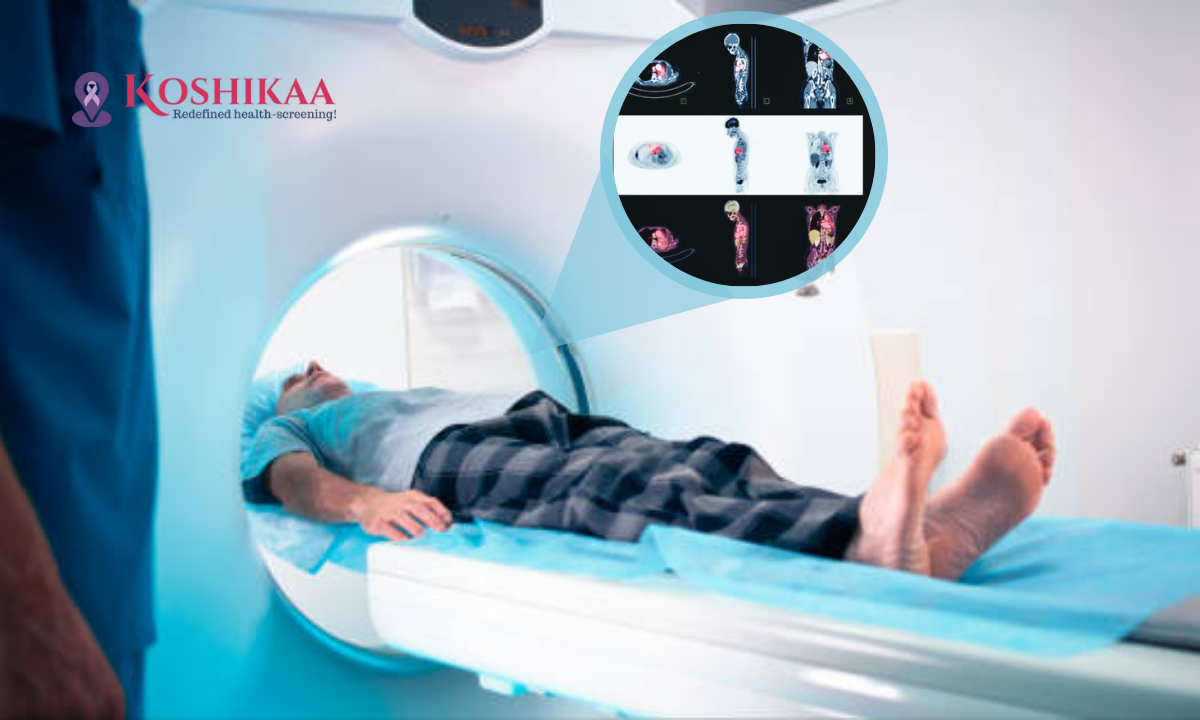
When facing a potential cancer diagnosis, getting accurate information quickly can be life-changing, and the PET CT scan has emerged as one of the most advanced imaging technologies for detecting and evaluating cancer.
This powerful diagnostic tool combines two sophisticated imaging techniques to give doctors unprecedented insight into what’s happening inside your body at both structural and cellular levels.
If you are seeking a PET CT scan in Bangalore for cancer evaluation, understanding how this technology works can help you feel more confident about the process.
Let’s explore the science behind PET CT scans and discover why oncologists worldwide rely on them for accurate cancer diagnosis and treatment planning.
Understanding What a PET CT Scan Means
PET stands for Positron Emission Tomography, while CT means Computed Tomography.
A PET CT scan combines these two imaging technologies into a single, comprehensive examination.
The PET component detects metabolic activity and shows how your cells are functioning, while the CT component provides detailed anatomical images of your body’s structures.
Together, they create a complete picture that shows not only where abnormalities are located but also how active they are metabolically.
How the PET CT Scan Test Works
The PET CT scan test uses a special radioactive tracer, usually a form of glucose called FDG, to detect cancer cells.
Cancer cells grow and divide rapidly, which means they consume much more glucose than normal cells do.
When the radioactive tracer is injected into your bloodstream, it travels throughout your body and is absorbed by cells that use glucose.
Cancer cells, being highly metabolic, absorb significantly more of this tracer than normal cells.
The PET scanner detects the radiation emitted and creates images showing areas of high metabolic activity.
These “hot spots” on the scan often indicate the presence of cancer, though they can sometimes represent inflammation or infection.
The PET CT Scan Process Explained
Understanding the PET CT scan process helps reduce anxiety and ensures you’re properly prepared for the examination.
1. Preparation Phase
You’ll be asked to fast for 4-6 hours before the scan, though you can usually drink water.
Avoid strenuous exercise for 24 hours before the test, as physical activity can affect how the tracer distributes in your body.
Inform your doctor about any medications you’re taking, especially if you have diabetes, as blood sugar levels need to be controlled.
Wear comfortable, loose-fitting clothing without metal fasteners to the appointment.
2. Injection and Waiting Period
Once you arrive at the imaging centre, a small amount of radioactive tracer will be injected into your vein.
You’ll then rest quietly in a comfortable room for about 60-90 minutes while the tracer circulates through your body.
During this waiting period, it’s crucial to remain relaxed and avoid talking or moving excessively, as muscle activity can affect the scan results.
3. The Scanning Phase
You will lie on a padded table that slides into the PET CT scanner, which looks similar to a large doughnut.
The scan itself is completely painless and typically takes 30-45 minutes to complete.
You must remain very still during the scanning to ensure clear, accurate images.
The machine will make some noise, but you’ll be able to communicate with the technologist through an intercom if needed.
4. After the Scan
The radioactive tracer leaves your body naturally through urine within 24 hours.
Drinking plenty of water after the scan helps flush the tracer out more quickly.
You can usually resume normal activities immediately, though some centres recommend avoiding close contact with pregnant women and young children for a few hours.
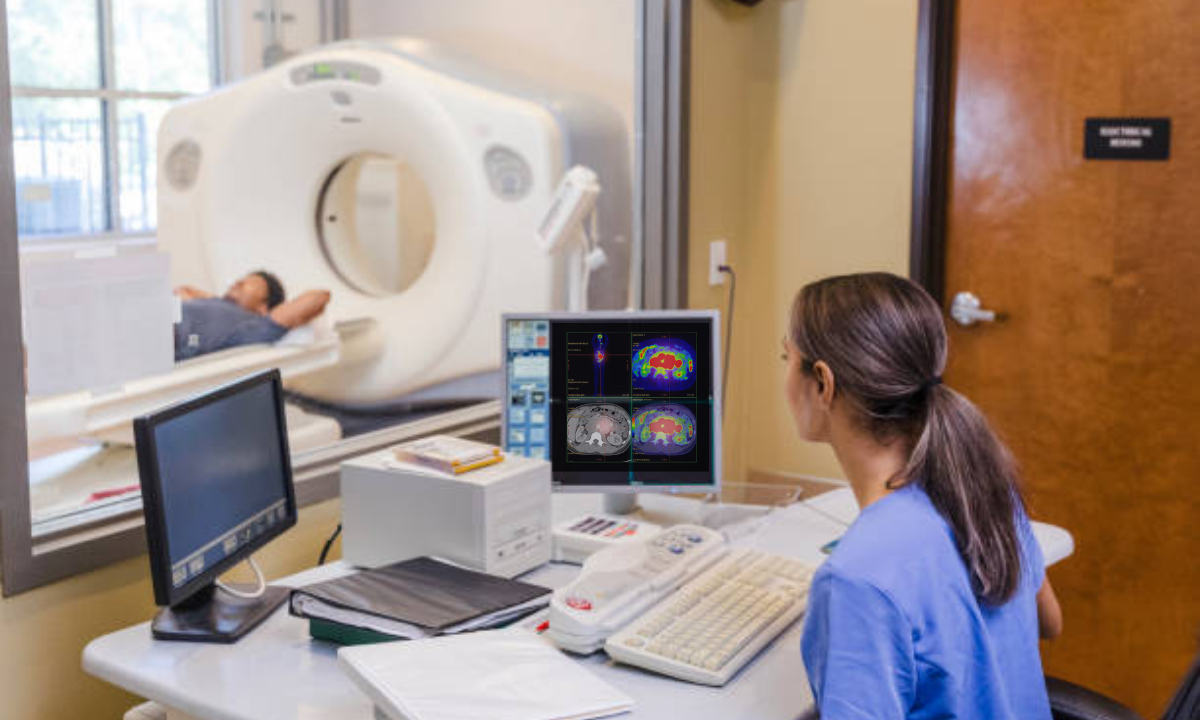
Interpreting PET CT Scan Results
Understanding your PET CT scan results is crucial for planning the next steps in your healthcare journey.
A specialized radiologist or nuclear medicine physician analyses the images and prepares a detailed report for your oncologist.
1. What the Results Show
Areas of high tracer uptake (hot spots) appear brighter on the images and may indicate cancer.
The scan shows not just the primary tumor but also whether cancer has spread to lymph nodes or other organs.
PET CT scan results help determine the stage of cancer, which is essential for creating an effective cancer treatment plan.
2. Limitations to Consider
While highly accurate, PET CT scans can sometimes show false positives due to inflammation, infection, or recent surgery.
Very small tumors might not be detected because they don’t produce enough metabolic activity.
This is why doctors often combine PET CT findings with other diagnostic tests and biopsies for confirmation.
Role in Cancer Treatment Planning
PET CT scans play a vital role throughout the cancer treatment journey, not just at diagnosis.
1. Initial Diagnosis and Staging
They help determine the exact location, size, and spread of cancer, which is crucial for staging.
Accurate staging ensures patients receive the most appropriate cancer treatment for their specific situation.
2. Treatment Monitoring
PET CT scans are repeated during cancer treatment in Bangalore to assess how well the therapy is working.
They can detect changes in tumor metabolism before changes in size become apparent on regular CT scans.
This early feedback allows doctors to adjust treatment plans if needed, potentially improving outcomes.
3. Post-Treatment Surveillance
After completing treatment, PET CT scans help detect any remaining cancer cells or early recurrence.
They distinguish between scar tissue and active cancer, which regular imaging sometimes cannot do.
Choosing the Right Diagnostic Centre
- When you need a PET CT scan in Bangalore, selecting a quality health screening centre in Bangalore is essential for accurate results.
- Look for facilities with modern PET/CT equipment and experienced nuclear medicine specialists.
- Check if the centre follows proper protocols for tracer preparation and patient safety.
- Verify that they provide detailed reports promptly and maintain clear communication with your referring oncologist.
- A good diagnostic centre will also explain the procedure thoroughly and address all your concerns before the scan.
Important Tips for Your PET CT Scan
Here are some practical tips to ensure your scan provides the most accurate results:
- Follow all fasting instructions carefully, as eating can affect tracer distribution
- Stay well-hydrated before and after the scan to help eliminate the tracer
- Inform the staff about any anxiety or claustrophobia you experience
- Bring a list of all medications you’re currently taking
- Arrange for someone to accompany you if you feel anxious about the procedure
Final Thoughts
PET CT scans represent a remarkable advancement in cancer detection and monitoring, offering insights that were impossible just decades ago.
While the technology is sophisticated, the goal is simple: to give your medical team the most accurate information possible to guide your cancer treatment journey.
If you have been recommended a PET CT scan in Bangalore, remember that this test is a powerful tool that helps ensure you receive the most appropriate and effective care.
At Koshikaa, we understand the anxiety that comes with a cancer diagnosis and treatment, which is why we are committed to providing advanced diagnostic services with compassionate care and accurate results.
Understanding how PET CT scans work empowers you to be an active participant in your healthcare decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Is a PET CT scan painful?
No, the scan itself is completely painless. You’ll only feel a small pinch when the tracer is injected, similar to any regular injection.
Q: How long does it take to get PET CT scan results?
Most facilities provide results within 24-48 hours. Your doctor will then discuss the findings with you and explain what they mean.
Q: Is the radiation from a PET CT scan dangerous?
The radiation exposure is minimal and considered safe for diagnostic purposes. The tracer’s radioactivity decays quickly and is eliminated within 24 hours.
Q: Can PET CT scans detect all types of cancer?
PET CT scans are highly effective for most cancers, but some slow-growing tumors or very small cancers may not be detected.
Q: How often can I have a PET CT scan?
The frequency depends on your specific medical situation. Your oncologist will determine the appropriate timing based on your treatment plan.