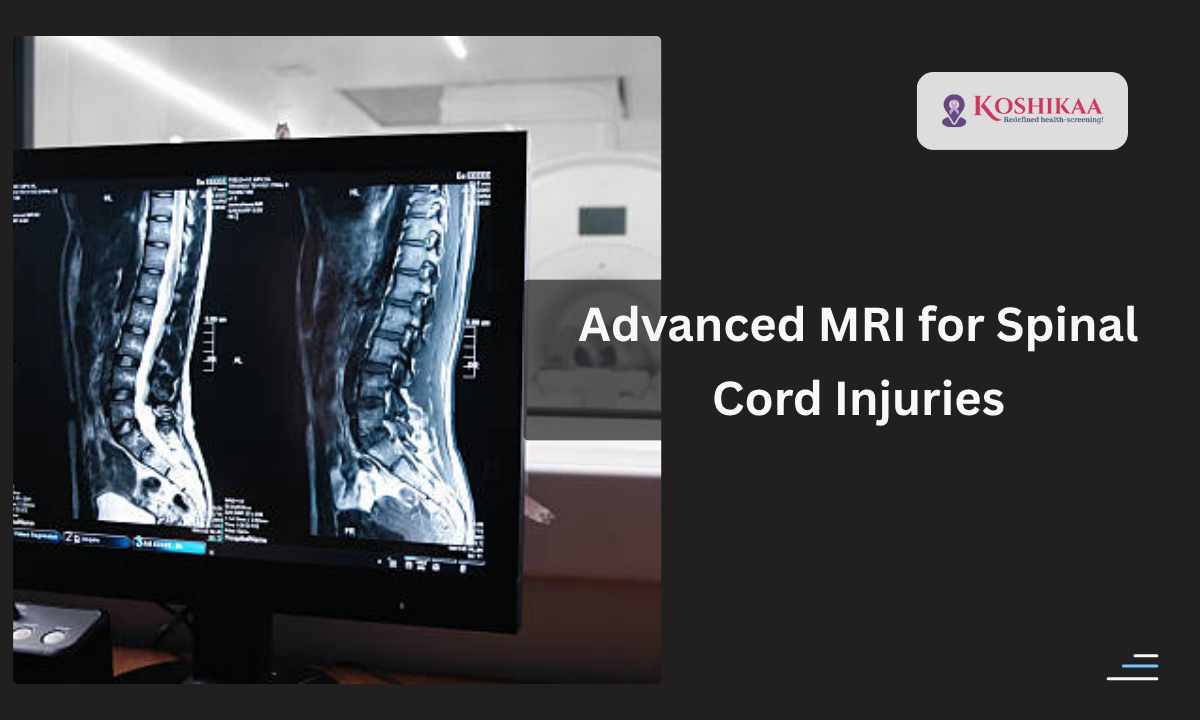
Spinal Cord Injuries Complications are often complex and require precise imaging for accurate diagnosis. With advanced MRI techniques, we can detect structural changes, assess the extent of damage, and guide treatment effectively.
At our best health screening centre in Bangalore, we use advanced MRI technology to help patients and doctors understand these complications.
Curious about how an MRI can uncover hidden problems in spinal cord injuries? Let’s explore.
Understanding Spinal Cord Injuries
A spinal cord trauma occurs when the spinal cord is damaged due to accidents, falls, or other injuries. The severity can range from minor nerve irritation to permanent paralysis.
Common spinal cord injury causes include:
- Road traffic accidents
- Sports injuries
- Falls from height
- Occupational hazards
Spinal cord injury symptoms can vary depending on the location and severity of the injury. Common symptoms include:
- Weakness or paralysis in limbs
- Loss of sensation
- Loss of bladder or bowel control
- Severe pain or pressure in the neck or back
Why Advanced MRI is Essential
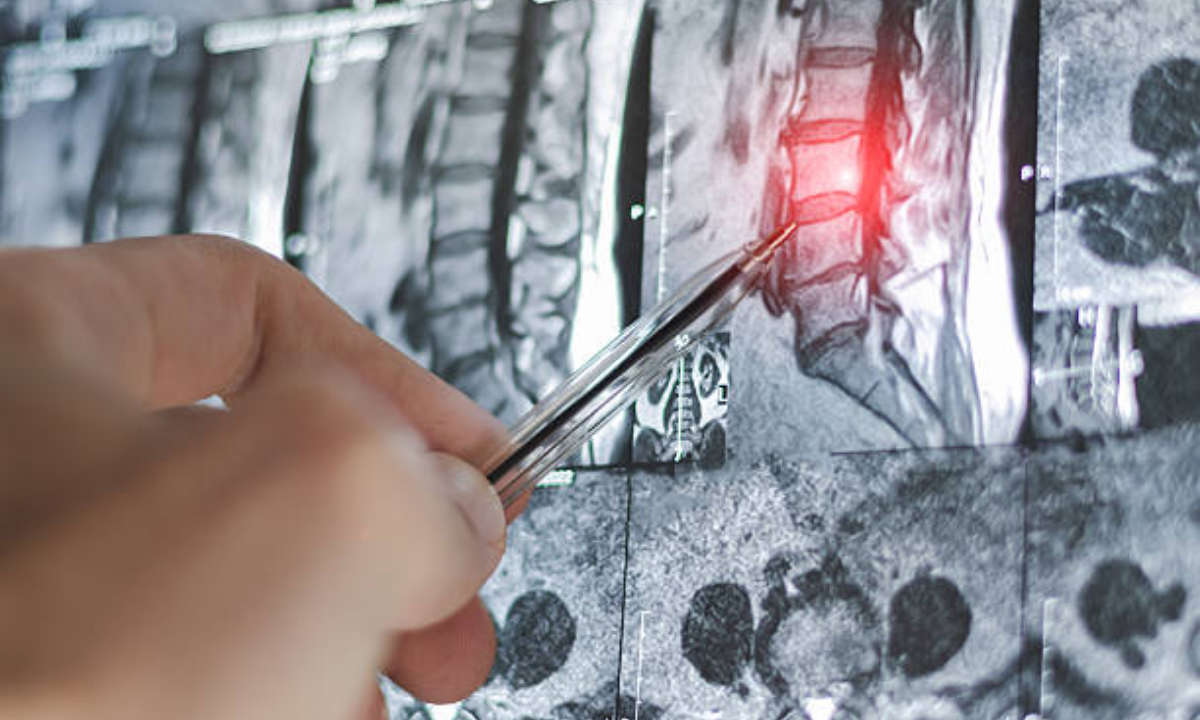
Imaging techniques like MRI are indispensable for evaluating spinal trauma management. Unlike X-rays or CT scans, MRI provides:
- Detailed soft tissue imaging
- Clear visualization of nerves and the spinal cord
- Early detection of secondary complications
Tip: MRI is particularly useful for assessing edema, hemorrhage, or ligament injuries that are not visible in CT scans.
Example: A patient with neck trauma had persistent numbness. While CT showed no fractures, MRI revealed subtle spinal cord edema, guiding proper rehabilitation.
What MRI Can Detect in Spinal Cord Injuries
| Complication | Detection through Advanced MRI |
|---|---|
| Spinal cord edema | Shows swelling and inflammation of nerve tissues |
| Hemorrhage | Identifies bleeding within or around the cord |
| Ligament or disc injury | Visualizes soft tissue tears or compression |
| Nerve compression | Detects pressure from vertebrae or disc herniation |
| Scar tissue formation | Tracks post-injury healing complications |
Tip: Regular follow-ups with MRI can help monitor progression and guide spinal cord injury management plans.
MRI vs CT for Spinal Cord Injuries
Many patients ask, “Is CT or MRI better for the spinal cord?”
- CT scans are excellent for detecting fractures and bone abnormalities.
- MRI scans are superior for soft tissue evaluation, including spinal cord edema, ligament tears, and nerve compression.
At our best MRI scan in Bangalore, we often combine imaging results with clinical assessments to ensure comprehensive evaluation.
Most Severe and Common Complications
The most severe complication of a spinal cord injury is permanent paralysis, which can affect mobility, bladder, bowel, and respiratory functions.
The most frequently observed complication is partial loss of sensation or motor weakness, which often requires long-term therapy and rehabilitation.
Tip: Early detection using advanced MRI significantly reduces risks of permanent damage by guiding timely intervention.
Duration and Safety of MRI
- Typically, a spinal MRI takes 30 to 60 minutes, depending on the area being scanned and whether contrast is used.
- The CT scan procedure is faster but may miss soft tissue complications.
Safety Note: MRI is non-invasive, radiation-free, and safe for most patients. Patients with metal implants should inform the technician.
Contrast in Spinal MRI
Sometimes, a contrast MRI is recommended to highlight areas of inflammation or abnormal tissue growth.
Tip: Drinking plenty of water before and after the scan helps flush contrast agents from the body.
How to Understand Your MRI Report
A CT scan report or MRI report includes details on:
- Spinal cord integrity
- Presence of edema or hemorrhage
- Disc herniation
- Nerve compression
If MRI results are normal, the report usually mentions “spinal cord signal normal” and “no evidence of hemorrhage, edema, or compression detected”.
Tip: Discuss every finding with your doctor or radiologist for proper interpretation.
Spinal Cord Injury Management
Spinal trauma management involves:
- Immediate medical care after trauma
- Surgery for stabilization if required
- Physical rehabilitation and occupational therapy
- Regular monitoring with advanced MRI
Example: A patient with partial paralysis underwent MRI-guided therapy. The scan revealed scar tissue formation that was addressed through physiotherapy, improving mobility within months.
Tip: Combining imaging with clinical evaluation ensures the best outcomes.
Choosing the Best MRI Scan in Bangalore
Patients seeking spinal imaging often ask, “What is the best scan for spinal cord injuries?”
We recommend advanced MRI because it provides:
- High-resolution images of spinal cord tissue
- Detection of complications that CT cannot reveal
- Guidance for surgical and non-surgical treatment
At our best health screening centre in Bangalore, we combine advanced MRI machines with expert radiologists to deliver accurate and timely results.
Wrapping Up
Spinal Cord Injuries Complications can be complex, but early detection and precise imaging using advanced MRI are critical for effective management. Choosing the best health screening centre in Bangalore ensures accurate scans and professional interpretation.
We, at Koshikaa, combine advanced MRI technology with patient-centred care to guide recovery, monitor complications, and provide peace of mind. For those dealing with spinal cord trauma, proactive imaging is key. Trust expert care to track, manage, and improve outcomes while keeping patients informed and safe.
FAQ Section
1. What is the most severe complication of a spinal cord injury?
Permanent paralysis affecting mobility, bladder, bowel, or respiratory function is the most severe complication, potentially requiring lifelong support and rehabilitation.
2. Is CT or MRI better for the spinal cord?
MRI is superior for evaluating soft tissue, nerve damage, edema, or hemorrhage, whereas CT scans are better for detecting fractures and bone abnormalities.
3. What is the most frequently observed complication of spinal cord injury?
Partial loss of sensation, motor weakness, or limited mobility are the most commonly observed complications, often requiring long-term therapy and rehabilitation.
4. How long does a spinal MRI last?
A spinal MRI usually lasts 30–60 minutes, depending on the area scanned and whether contrast is used, and is non-invasive and radiation-free.
5. When to worry about MRI results?
Abnormal signals, spinal cord compression, or persistent neurological symptoms after trauma indicate the need for urgent medical consultation and follow-up scans.