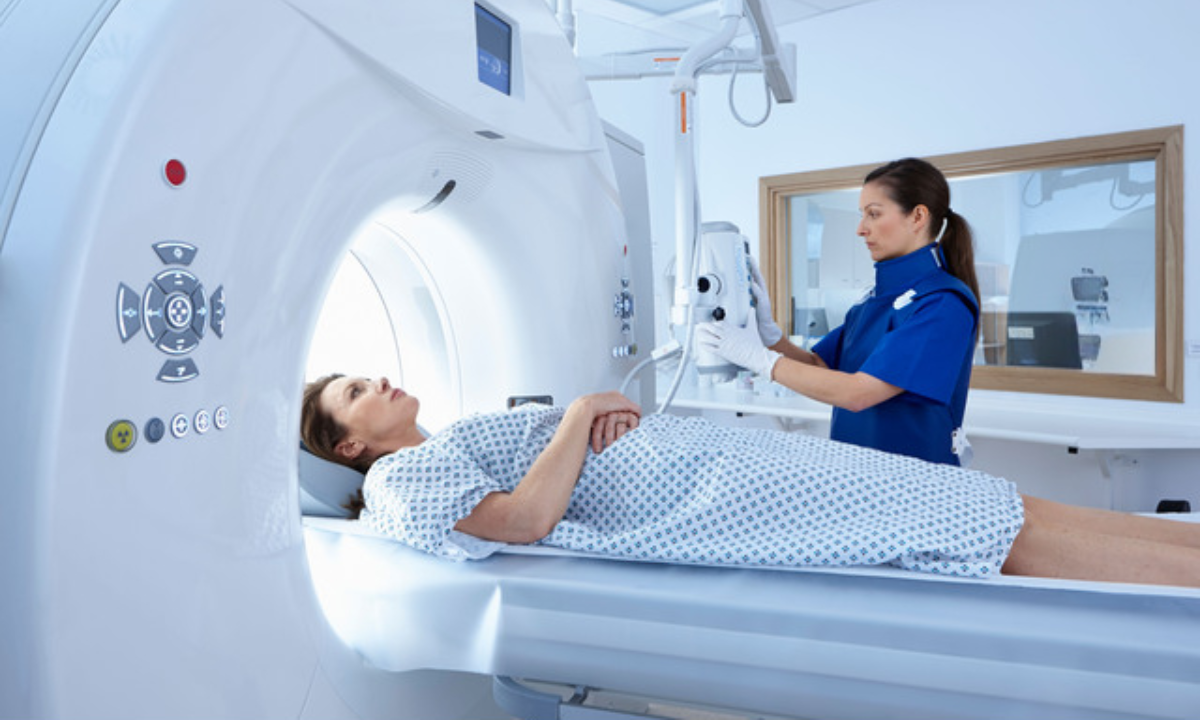
A CT abdomen and pelvis is one of the non-invasive imaging tests, which utilizes X-ray and computer processing to generate a cross-sectional image of the body. An abdomen and pelvis scan is a test ordered by a physician that leaves many patients wondering what this test is. Simply put, it is a combined examination of the organs, blood vessels, and bones in your chest and the hips to assist in the diagnosis of any pain, injury, infection, or disease.
The current article will take you through the preparation of the patient to the interpretation of results in a simple step-by-step approach.
Understanding These Two Tests

Abdomen and Pelvis Scan: What is it?
Knowing the meaning of an abdomen and pelvis scan may help you relieve anxiety when a doctor prescribes an imaging procedure. Examples of structures that are normally checked using this scan include the liver, spleen, kidneys, bladder, intestines, reproductive organs, and surrounding blood vessels. In contrast to an ultrasound that involves sound waves or an MRI image used with magnetic fields, this examination takes advantage of computed tomography in high-resolution detail.
Key Components of the Scan
- Contrast Material: A dye can be injected in order to show the blood vessels and particular tissues.
- Scan range: The machine rotates around your midsection, starting a bit over the diaphragm and going to mid-thigh.
- Image Quality: Slices of information, which are but a few millimeters thick, will be merged into 3-dimensional figures.
Prepare Yourself For Scan
Proper preparation will ensure proper images and proper results. The following is a simple checklist on patient preparation for a CT scan:
1. Fasting: You might be requested to fast or go without intake of food or water for 4-6 hours.
2. Medication Review: Remember to state any medicines you take, both prescription and over the counter, and any allergies to the provider.
3. Accessories (dressing, etc.): Remove all metals and metal jewelry and eyewear, and wear loose, comfortable clothes.
To get a better outcome, patient preparation for a CT scan is likely to include the consumption of oral contrast or wearing a gown. Concise directions facilitate the reduction of delays and duplication of the scans.
Having a CT scan is usually frightening. It is helpful to know what steps to take.
Step 1: Arrival and Registration
- He or she will complete forms and chat about your history.
- When contrast is employed, a small IV line is inserted into your arm.
Step 2: CT scan abdomen procedure
- You are placed on a long, thin table, which slides into the CT machine.
- The technologist can also give you some advice to hold your breath briefly so as to avoid the blurring of the scanner.
Step 3 CT scan pelvis procedure
- To attack your lower pelvis, the table is set up.
- More contrasted/sequential images can be taken as and when required.
Time acquisition and CT scan duration
The entire protocol lasts 15 -30 minutes to set up the device and carry out follow-up checks after the scan. The X-ray certification takes only seconds, but positioning and contrast injections add time.
Difference between abdomen CT and CT pelvis
CT abdomen
- Examines organs above the hip bones (such as the liver, pancreas, and spleen).
- Typical of pain, cancer/tumors, or inter-bleeding.
CT pelvis
- Concentrates on the bladder, reproductive organs, lower intestines, and the pelvic bones.
- As with any pelvic pain, urinary trauma or issues.
- Having both scans simultaneously captures the entire picture and the possibilities of other tests being unnecessary hasten the process of diagnosis.
What is diagnosed by a CT scan?
Upon a CT scan, it may:
- Determine the malignant and benign masses as well as tumors.
- See spot inflammation and infection (appendicitis, diverticulitis, or abscesses).
- Determine vascular complications (aneurysms, blood thrombosis, or vessel obstruction).
The question most patients frequently ask is what CT scans can detect other than their tumor. They can display fluid masses, organ swelling, and structural deviation.
Safety Considerations
1. Radiation We are exposed to Radiation; doses are regulated and exceed random X-rays.
2. Contrast Reactions: There is a small likelihood of an allergic reaction to dye, but in the case of this rarity, your care team is ready to react.
3. Pregnancy: Pregnant women need to talk to the provider to find out risks and options.
Better where to get/ scanned
There are locations with different access to quality imaging. When considering choices on CT scan in Bangalore, the following are some elements to consider:
• Accreditation: Search out those centers that are nationally accredited in imaging services.
• Technologist Skills: Experienced workers are required to offer a proper technique, as well as comfort to the patient.
• Turnaround Time: Effective delivery of reports within a brief period can accelerate the process in making the right decision in terms of treatment.
Numerous hospitals in India are providing CT scan in Bangalore with advanced machines that have low-dose protocols and quick image reconstruction. Coverage and prior-authorization needs should never be in doubt.
Tips for Hassle-Free Experience
1. Be on Time: Doing the forms carefully will do away with stress.
2. Hydration: The passage of IV contrast can be alleviated and dye flushed by hydration unless one is fasting.
3. Ask Questions: Clarify any doubts within your mind regarding the method of CT scan abdomen or pelvis scanning process before you go.
Improving Your Diagnostic Journey
Once you finish your CT abdomen and pelvis scan, it is important to have knowledge of further steps in order to make informed decisions. Talking with your physician about your results as soon as possible will ensure that something out of the ordinary is handled immediately. There are quite a number of centers where you have the option of digital access to photos and reports, and thus you can review them at home.
Hydrating well post-scan assists in flushing any residual contrast dye. If you experience unusual symptoms like rash or breathing difficulty, notify staff immediately. Inquire about follow-up imaging schedules to monitor conditions or treatment progress. Keep a copy of your scan in a secure file for future reference and comparison. Store a copy of your scan(in a safe file) to compare in the future.
Conclusion
Having a scan of the tummy and hips might appear complicated, but knowing what to expect in each step, like preparing the patient before a CT scan, and the detection capacity of CT scans, could calm your nerves. If you require a CT pelvis to assess a question of injury to a bone or a CT abdomen to look into abdominal pains, this examination provides quick and accurate information.
In case you want to find a CT scan in Bangalore or any other area, you should focus on a place or center that has well-trained and competent personnel with modern machines. With this knowledge, you will feel confident with your appointment.
To individuals who may require a CT scan in Bangalore, Koshikaa Screening Center offers customized facilities and radiology services to facilitate the accomplishment of accurate and exact results. Necessary procedures should also be followed to ensure insurance coverage and preauthorization requirements are verified before scheduling. Ask yourself questions on technology, report turnaround, and radiation-dose optimization to get as many benefits out of a scan as possible, including sedation options, should you wish.