The fight against breast cancer is a vital tool in mammography. It is also a specialized medical imaging procedure utilizing low-energy X-rays to examine the breast tissue as the first line of investigation for early detection and diagnosis. Read this guide to learn how mammography in Bangalore works, the benefits, what to expect in the procedure and the benefits of the examination.
What is Mammography?
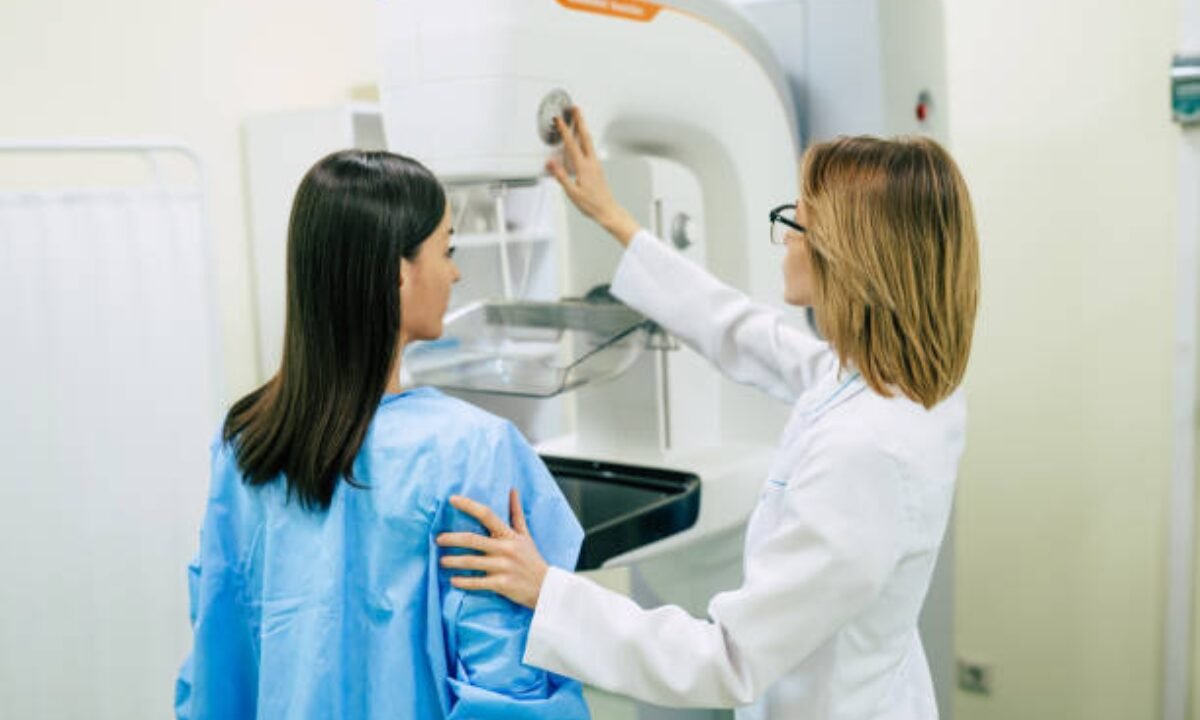
Mammography works to make images of the breast tissue. These images assist in the discovery of any abnormal situation that may suggest the existence of breast cancer or other sicknesses. Early identification of these problems raises the probability of success of treatment and recovery.
Types of Mammography
There are several forms of mammography in Bangalore:
- Digital Mammography: This advanced option is a digital detector converting X-ray signals to electronic images that can be stored and shared easily.
- 3D Mammography (Tomosynthesis): This innovative technique uses multiple images of the breast from different angles to obtain a more thorough exam. Women with dense breast tissue find it especially helpful.
- Screening Mammography: This form is recommended for women who do not have symptoms and is completed regularly (usually yearly) to detect potential problems early.
- Diagnostic Mammography: This is used, for women with symptoms such as lumps or pain, to focus on areas of concern.
How Mammography Works?
The mammography process involves several essential steps:
1. Preparation: They recommend women don’t apply deodorants, lotions, or powders before the exam as they can interfere with the image process.
2. Positioning: The patient stands in front of the mammography machine during the exam. A technologist applies gentle pressure to a flat surface to position the breast and flatten the breast for better imaging.
3. Imaging: Typically, X-ray images taken from 20 different angles are taken within 20 or so minutes. That compression can be uncomfortable but it is necessary for producing clear images.
Analysis: The images are then captured and a radiologist reviews any abnormalities. Further testing may include a biopsy if suspicious findings are found.
Benefits of Mammography
Mammography has many benefits when it comes to maintaining breast health. Consider the following advantages:
1. Breast Cancer Early Detection
Mammography is the most significant advantage in the sense that early detection of breast cancer is possible. The earlier the diagnosis, the better — they can intervene earlier.
2. Reduced Mortality Rates
Mammography is shown through research to reduce breast cancer mortality by approximately 15–30%. Early detection allows women to get needed treatment earlier when it’s still possible to control cancer.
Increased Treatment Options
Women who have breast cancer when it’s detected early have more options for treatment. When necessary, they may opt for more aggressive treatments, or choose between less invasive procedures such as lumpectomies. Early detection means getting a less aggressive treatment, which also improves overall quality of life.
Monitoring Changes Over Time
Mammograms are vital to the surveillance of women with a family history of breast cancer or other risk factors. Healthcare providers can track any changes in breast tissue over time with regular screenings, which gives early warnings about any potential developments that should require further investigation.
Peace of Mind
Mammography screenings also give women peace of mind about breast health. Significantly they help reduce anxiety and are involved in making you feel better overall.
How is Mammography Performed?
Understanding what to expect can help alleviate anxiety related to the mammography process:
- Duration: The appointment generally takes about 20 minutes, so it’s a short appointment.
- Comfort Levels: While breast compression can be uncomfortable, it’s brief and the benefits are trivial compared to that little discomfort.
- Post-Procedure: Women can return to their normal activities immediately after the mammogram. Their results usually come out within a few days.
Who Should Get Screened?
At a woman’s general risk, screening recommendations vary, but, in general, women should begin annual mammograms at age 40. People with family histories of breast cancer may have to start screening early or may need some other method, like MRI, along with a normal screening to make sure that their breasts are being monitored properly.
Overcoming Barriers to Mammography
However, mammography remains a crucial screening despite barriers preventing women from accessing it. To improve breast health outcomes and encourage women to get their screenings, it is important to address these challenges.
1. Access to Care
Geographic, financial, or logistical barriers frequently make it difficult for many women to access a healthcare facility. Communities can improve access by:
- Mobile Mammography Units: Increasing accessibility can be done by implementing mobile units that travel to underserved areas and higher screening rates can be achieved for already underserved women.
- Insurance Coverage: Along with being able to go to get a routine screening, comprehensive insurance coverage for mammograms can enable women to afford to see a doctor when they seek care, and lobbying for this insurance coverage can help do that.
- Community Initiatives: Through the programs, local organizations can become local outreach mothers to help inform women of the importance of regular screenings by offering free and discounted mammograms.
2. Fear and Misconceptions
Women are afraid of the procedure and get scared away by misconceptions of what mammography is about. To combat these issues:
- Education: Dispersing myths by providing clear, factual information about what to expect with a mammogram and reducing anxiety can help. Clinics and community health organizations should have easy access to educational resources.
- Peer Encouragement: Women can be encouraged in support groups and personal testimonies to seek out mammograms, schedule their own, and put their health a higher priority.
3. Cultural and Personal Beliefs
A woman’s decision to take up mammography is influenced by cultural attitudes and personal beliefs about healthcare. Initiatives should focus on:
- Culturally Sensitive Outreach: Adapting education and outreach programs so they are culturally relevant can make breast health less alien to individuals; thereby promoting understanding of the importance of breast health.
- Engagement by Healthcare Providers: Healthcare providers would be effective if they led an open conversation with patients about their doubts and beliefs, and cultivated a relationship based on trust and clarity.
Conclusion
Mammography in Bangalore is so much more than just a medical procedure as it serves as a means to early detection of breast cancer and is an essential part of women’s health care. And this is where advanced technology comes into play, to make sure mammograms are efficient and accurate and help to spot early potential health issues.
Early detection, lower rates of mortality, a range of advanced treatment options available, continuous monitoring, and peace of mind all benefit from the widespread use of mammography in women’s health. Knowing how the process works and participating actively in regular screenings provides women a means to be in charge of their breast health and make a big difference in their likelihood of a good outcome.
It’s recommended that women talk with their healthcare providers about when screening should start and be diligent about staying vigilant of their breast health.
Breaking down barriers to mammography access and creating an environment of education and support will help women everywhere to have good breast cancer outcomes.
An ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure—regular mammograms are important so women and their families can lead a healthier future.
Mammography is important, let the others know how important it is and we try this together and support each other to ensure we are pro-active in our health and well-being. By joining together, we can make progress towards a world with easier detection and treatments for breast cancer, for all women.
Offering pet CT scan in Bangalore, Koshikaa provides accurate diagnostic imaging for complete cancer evaluation and management.

